8 Types of Market Segmentation: Explained & Explored

Different types of market segmentation allow companies to understand their market better and create more effective messaging, products, and marketing campaigns.
Knowing which methods of market segmentation are right and when to use each helps you make the right moves at the right time. So, if you’ve decided to segment your market, let us explain the various ways to do it and get you on the path to success.

Types of market segmentation
The four most common types of segmentation include demographic, behavioral, firmographic, and psychographic. However, as technology advances, along with the expectations of modern consumers, it’s important to know all the ways you can segment your market, which is why I’ve detailed eight ways to segment a market.
If you’re completely new to this process, I’d recommend you look at our other post covering the ins and outs of what market segmentation is before you choose which type of segmentation is best to use.
Even if you’ve already divided your market based on certain parameters or similar characteristics, it’s worthwhile to take a step back and remember that an audience analysis strategy often benefits from a combination of tactics in the digital world.
1. Demographic segmentation – who is buying?
Typically, segmentation starts with demographic audience analysis – it’s usually what we first think of when defining our customer personas. Geographic segmentation forms part of this, although it’s often referred to in its own right. This type of market segmentation sticks to basic characteristics that can be easily identified:
- Age
- Gender
- Ethnicity
- Income level
- Marital status
- Family size
- Education level
- Location
Demographic segmentation is useful for deciding how to target marketing or services to particular people or groups. It helps understand how different groups of people respond to different messages, products, or services. For example, suppose a business wanted to target a certain age group with a particular product or service. In that case, demographic segmentation could help them identify the right audience and tailor their messaging accordingly.
It’s ideal for B2C companies in particular. You’ll have greater chances of success (i.e., getting your customers to purchase your offering) when whatever you’re putting in front of your audience resonates with them.
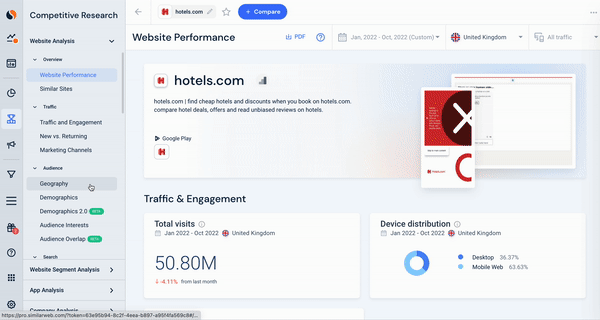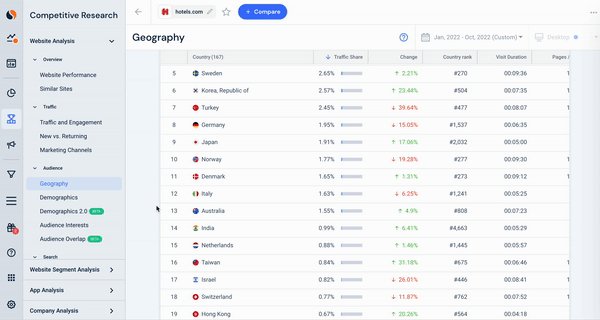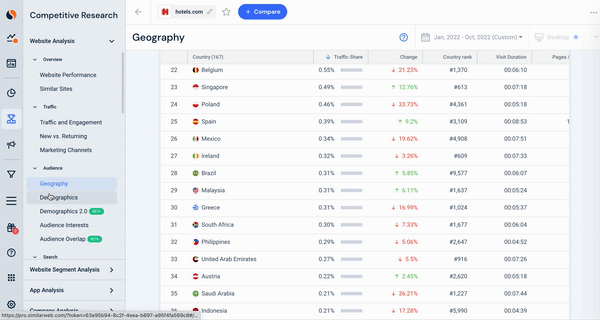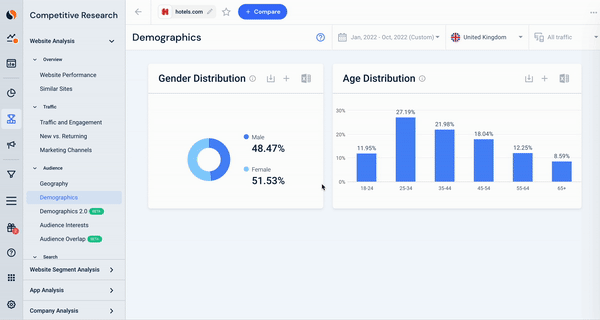
Here, we see hotels.com traffic data, looking specifically at the geographical breakdown of their visitors, combined with a snapshot of their audience’s gender and age distribution. This data can be utilized to segment any audience to see which countries drive traffic and the split of that audience’s characteristics.
2. Behavioral segmentation – how are they buying?
Behavioral segmentation is a great way to gain insight into the actions and behaviors of consumers. It can be used to identify buying patterns and preferences and tailor products, services, and marketing messages to specific customer segments. Additionally, it can help companies better understand which customers are most likely to respond to certain campaigns or promotions.
It’s an ongoing process of collecting and analyzing behavioral data. Over time, the data you collect will reveal more about your consumers, such as:
- Purchasing habits
- Browsing behavior
- Interaction with your brand
- Interaction with your competitors
- Buying history
An ecommerce site or retailer, for example, may make segments based on the channel or device people use to reach its site. In contrast, a gaming site might segment according to the frequency of purchases or which competing gaming sites users visit.
One example of behavioral segmentation is segmenting customers based on their purchase frequency. This could involve creating segments such as customers who purchase once a month, a quarter, or annually. This helps companies understand the different types of customers it has and tailor its marketing and product offerings accordingly.

Similarweb’s audience overlap feature is a great way to see a snapshot of how an audience overlaps with others in your space. You can quickly compare your own audience with that of key rivals, to see how loyal consumers are within a market.
3. Firmographic segmentation – what types of companies are buying?
If you’re a B2B company, you will be less interested in your prospects’ individual, personal characteristics. Your buyer is a company, and you need to understand the character of that business rather than the individuals who comprise it.
Firmographic segmentation goes hand in hand with company research. It analyzes the industry, company size, revenue, location, and history of your potential customers.
For example, a company may decide to segment customers by revenue size. Companies with higher revenues could be placed in the high-value segment, while those with lower revenues would be placed in the low-value segment. As a result, it can tailor its resources and marketing efforts accordingly.
4. Psychographic segmentation – why are they buying?
It’s a tough question to answer. But understanding the motivation of your target audience is key. Some factors that influence why customers buy from you could include the following:
- Lifestyle
- Values
- Beliefs
- Interests and Hobbies
- Political orientation
- Goals
Of course, you’ll only need to focus on the ones that are relevant to your industry. An example of how to do psychographic segmentation would be to divide a market of luxury car buyers into three distinct groups:
- Aspirational: These customers aspire to own a luxury car and are more likely to be influenced by luxury car advertisements.
- Sophisticated: These customers are knowledgeable about luxury cars and prefer to spend time researching and evaluating their options.
- Traditional: These customers prefer a more classic look and feel for their luxury cars, and are likely to be driven by word-of-mouth recommendations.
5. Transactional segmentation – how do they transact?
When it comes to online shopping and eCommerce sites, transactional segmentation keeps all the receipts. It considers payment method, purchase value, use of coupons or special offers, and transactions based on categories or top-selling products. It’s a type of segmentation that can optimize pricing strategies and measure customer retention.
One way to do transactional segmentation is to look at customer purchase history. For example, if you’re an apparel retailer, you can look at the types of items customers purchase and create segments based on that. This may include a segment for customers who mostly purchase dresses, another for those who purchase pants, or another for those buying a variety of items. You could then use these segments to tailor marketing messages and offers to each customer group, helping to increase engagement, the relevance of messaging, and sales.
6. Technographic segmentation – what type of tech do they use?
Technographic segmentation is the process of segmenting customers based on the technology they use. This can be done in several ways.
One example would be to segment customers according to the operating systems they use. For instance, if you are a software company, you could segment customers based on whether they use Windows, Mac OS, Linux, Android, etc. You could also segment customers according to the software or device they use.
Utilizing Similarweb’s Data-as-a-Service enables companies to conduct technographic segmentation with greater accuracy by providing detailed data on the technologies that target audiences use. This includes operating systems, software, and device preferences, helping to craft highly targeted tech-based marketing strategies.
7. Seasonal segmentation – when are the peak periods of interest?
Some industries are strongly impacted by the seasons and divide their target markets accordingly. We’re not just talking about weather or holidays, though. Consider cultural, sports, or political events that stir human interest and alter buying behavior.
While it’s not relevant to every business, certain industries like travel, accommodation, finance, and retail are highly impacted by seasonal trends.
Some of the benefits of this type of market segmentation include:
- Increased focus: Focus efforts on specific customer segments during certain times of the year helps ensure the right message reaches the right audience at the right time.
- More effective targeting: Better target consumers with more relevant and timely content while improving customer engagement.
- Improved budgeting and resource allocation: Better planning and allocating of budgets and resources to drive focus on promotions with the potential to yield the best results.
- Increased efficiency: Streamline marketing efforts for a more efficient process.
- Increased profitability: Generate higher profits with targeted offers and campaigns.
8. Benefit segmentation – what benefits do people respond to?
This type of market segmentation is based on the potential benefits a customer receives. While it’s sometimes considered a type of behavioral segmentation, it’s worthy of a mention in its own right.

An example is when customers are segmented based on their preferred benefits, such as loyalty rewards or discounts.
For instance, a company may have a loyalty program that offers discounts or rewards to customers who have shopped with it for a certain amount of time or who have reached a certain spending threshold. They may have a different program for customers who prefer free shipping or early access to new products. By segmenting customers based on their preferred benefits, the company can tailor its marketing efforts to target customers more effectively and increase sales in tandem.
Another way to look at this type of segmentation is by the perceived benefit a product offers to a customer. The supplement sector gives us a great example of this to showcase.
Let’s say a company offers a range of health supplements, some for weight loss, some for muscle gain, and some for anti-aging. In this instance, a company could perform segmentation based on the benefits a customer is seeking. This way, should they offer similar products with the same benefits, they have a readily available market to take them to.
Choosing the right type of market segmentation
The best type of market segmentation to use depends on your business and your overall objectives. Here are three easy steps to help you determine which market segmentation techniques are right for you.
- Consider the characteristics of your target audience, the benefits of your offering, and the goals you want to achieve.
- Analyze your market data to determine the best characteristics to use for segmentation.
- Once you have identified the most relevant characteristics, you can develop a segmentation strategy that fits your objectives.
Market segmentation bloopers to avoid
Before you take a swing at segmenting your market, here are a few common missteps to avoid:
1. Don’t rush.
Make sure that you’ve completed each step in market segmentation before moving on to the next one.
2. Don’t forget to optimize.
Creating your market segmentation strategy requires considerable initial effort, but don’t stop there. It’s tempting to stick with the same segmentation for good, but markets are dynamic, so keep your finger on the pulse and keep optimizing. You need to identify upcoming trends and emerging markets, detect shifts in behavior and preferences, and, most of all, keep an eye out for up-and-coming competition. Measure performance and apply changes if required.
3. Don’t limit yourself to small segments.
Be careful not to create segments that are too small. The temptation to add factors and metrics for better targeting can lead to splitting your audience into endless, tiny categories. Instead, aim for actionable insights that impact your company on a large scale.
4. Don’t ignore the data.
The backbone of effective market segmentation is your research and analytics strategy. No matter which of the different types of market segmentation you go with and how you combine them, data quality is essential. It all starts with analyzing your audience. You’ll discover natural groupings in your audience, and with a bit of market research, you can find out if these match the industry standards.
Similarweb for market segmentation
Before starting any market segmentation, you need credible data about your rivals and market. While secondary information is readily available, the freshness of that data is often lacking, and that means any analysis has the potential to be irrelevant and out of date.
Dynamic market data changes the game–with the power to help companies shift from reactive to proactive. When businesses need to do more with less, market segmentation allows you to pinpoint opportunities for growth and uncover prospective channels to hone in on.
Similarweb allows you to zoom in on the segments that matter most to your business; so you can easily draw out actionable insights to inform your strategy and power up your segment analysis.
Feature Spotlight: Segment Analysis
- Analyze the performance of a specific topic, category, brand, or line of business on any website.
- Compare performance within a customized industry and benchmark your own performance to spot opportunities and efficiencies.
- Get granular insights that allow you to quantify the impact of specific campaigns or offers over time, and make rapid changes when markets shift.
Here’s how it works.
FAQ
Why is market segmentation important?
Market segmentation is important because it allows businesses to effectively target their products and services to the right customer base. By understanding their target market, businesses can tailor their offerings to meet the needs and wants of their potential customers, increasing the likelihood of success.
Why should you use different types of market segmentation in business?
Businesses should use various types of market segmentation as it enables more effective marketing campaigns. Mixing up the types of segmentation facilitates a better understanding of a target audience and informs messaging that is tailored to the unique needs of a subset of a target market.
What are four common market segment examples?
Four common market segment examples include geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral. Geographic segmentation looks at where customers are located; demographic segmentation looks at demographic characteristics such as age, gender, and income level. Psychographic segmentation looks at lifestyle and personality traits, and behavioral segmentation looks at how customers interact with a product or service.
What are the different types of market segmentation?
The different types of market segmentation are demographic, psychographic, firmographics, benefit or value, transactional, technographic, seasonal, and behavioral.
Track your digital metrics and grow market share
Contact us to set up a call with a market research specialist







