How to Use Heading Tags? Best Practices for SEO

Every content writer and SEO expert shares a common goal: to craft content that both hooks readers and performs well in search engines. But let’s be real – sometimes, those SEO insights and tactics get overlooked or done halfway.
One simple, yet often underutilized, method to improve both readability and SEO? You guessed it: heading tags. These little HTML elements might seem minor, but when used right, they work wonders by structuring your content and making it easier to digest for readers and search engines alike.
In this guide, we’ll break down the best practices for using heading tags. Master these, and your website will be on the fast track to better search rankings and a smoother user experience.
Let’s head(ing) straight on to what you need to know.
What is a heading tag?
In simple terms, heading tags are HTML elements (<h1> to <h6>) that create a hierarchy of your content. They don’t just give structure—they give context, helping both readers and search engines understand what’s important.
The <h1> tag is your headliner – the main idea of your page – while <h6> sits at the bottom of the hierarchy. It might seem basic, but if you skip these, your content can feel like one big block of text, making it harder for humans and algorithms to get through.
If you don’t format your content with heading tags, it will be very difficult for humans and search engines to understand.
In terms of SEO, if you structure your paragraphs and define your importance and the structure of the content within the page. This is specifically important for search engines. If you structure your information into readable, hierarchical sections of the page, it will help the search engine to crawl and index your content.
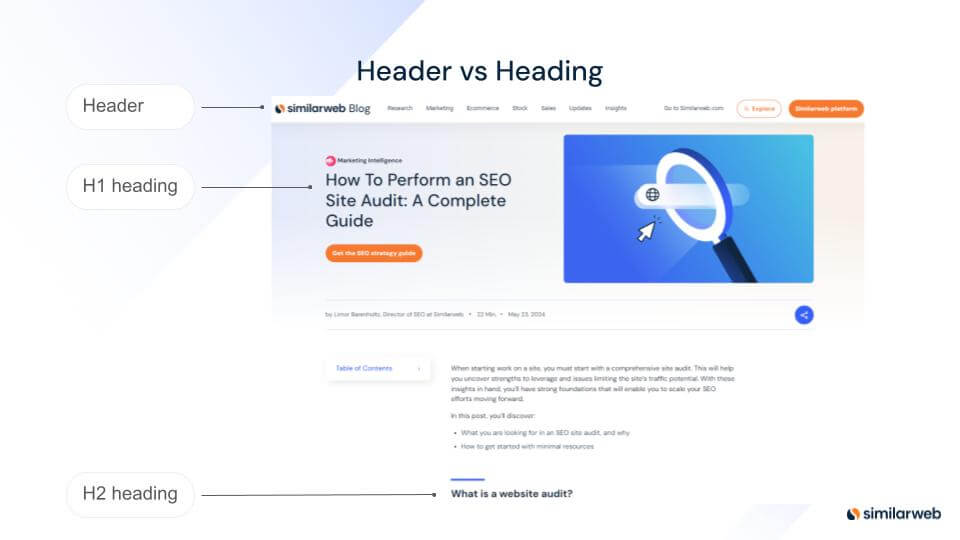
What’s the difference between a heading tag and a header tag?
Heading tags (<h1> to <h6>) define the content hierarchy on a page, indicating which parts are most important for both users and search engines. For example, the <h1> tag represents the main heading, while <h2> to <h6> are subheadings. Using these tags correctly is crucial for Technical SEO, as they help search engines understand your page structure.
Header tags, on the other hand, use the <header> element to define the webpage’s structure, typically containing elements like navigation links, logos, or search bars. Understanding the difference is key because improper use can impact both user experience and SEO. Heading tags organize content, while header tags shape the layout of key webpage sections.
Why use headings?
Using headings is an on-page SEO best practice. If you want to structure your content properly, create a better user experience, and optimize your content for search engines, headings are the way to go. Here’s why.
1. Use headings to show structure
Headings create a roadmap for readers, helping them jump to the parts they’re interested in. Whether someone’s casually skimming or searching for specific info, your headings guide them, keeping them on your page longer. And let’s face it – people trust content that’s clean and easy to read.
2. Use headings to improve your user experience
Most visitors don’t read every word—they skim. Well-placed headings let users find what they need without scrolling through endless paragraphs. If users can quickly get what they want, they’re more likely to stay, read other pages, and engage more with your site.
3. Optimize for featured snippet
You know those boxes at the top of Google search results? They’re called featured snippets, and they can drive a lot of traffic to your site. Search engines look closely at your headings to figure out if your content answers a query well enough to appear there. Write clear, keyword-rich headings, and you might just land that coveted snippet spot. So, optimizing for featured snippets is a great way to increase organic traffic to your site.
4. Use headings to highlight your keywords
Headings are prime spots to use your keywords. Not all locations in your content carry the same weight for SEO, so placing keywords in headings, especially in higher-level ones like H1 or H2, is more impactful than just including them in the body text. While adding a keyword to an H1 is stronger than an H4, both are better than only using the keyword once in the content. This strategic placement helps search engines better understand the focus of your page and boosts your chances of ranking higher.
5. Use headings to improve your rankings on Google
Headings help search engines better crawl and index your content, boosting your chances of ranking higher in search results. A well-structured heading format enhances SEO, driving more organic traffic. Plus, rich snippets often use headings to present key information, making them crucial for modern SEO.
Heading structure and heading tags hierarchy
A clear heading structure is easy to implement and key to organizing your content effectively. A proper hierarchy not only improves readability but also boosts your SEO.
Heading tags (H1-H6) divide your content into levels, making it easier for both users and search engines to understand. Here’s how to structure your headings:
H1 tag
Your main heading—used only once per page—should describe the core subject and include your primary keyword for a strong SEO impact.
H2 tags
These break the content into primary sections. You can use multiple <H2> tags, often incorporating secondary keywords to capture more search terms.
H3 tags
Used within <H2> sections, H3 tags further subdivide content. These subheadings help readers find details and stay engaged, especially in longer articles.
H4-H6 tags
These tags provide even finer content subdivisions, useful for technical documents or detailed guides. They’re used less frequently but can enhance content structure when needed.
Heading tags hierarchy example
To create a clear structure for your content, follow a proper heading hierarchy. The rule is simple: use the <h1> tag for the main topic of the page, then organize subtopics under <h2>, and more specific details under <h3>, continuing as needed through <h6>. This hierarchy helps both users and search engines easily understand and navigate your content.
Here’s an example using pasta shapes:
As you can see, “Pasta Shapes” is the main topic, with “Long Pasta” and “Short Pasta” as subcategories, and specific pasta types like “Spaghetti” and “Penne” listed as details under their respective categories.
This structure makes content easy to follow, improving user experience and SEO. By keeping a logical hierarchy, your pages become more scannable, and search engines better understand the focus and relevance of your content.
HTML heading tags best practices
Follow these tips to ensure your headings boost your SEO efforts:
1. Use your keywords in your headings
Sprinkle your primary and secondary keywords throughout your headings. This not only makes your content more readable, but also tells search engines what your content is about. It’s easy to stuff your headings with keywords and it probably wouldn’t hurt. But your headings will look stiff and your content will suffer. Instead, use enough keywords to feel natural in the context of the heading, without overdoing it. You’ll have better-optimized, better content. It will also become more usable and, hopefully, rank higher for more search queries. This will increase your organic traffic.
Pro Tip: Try featuring long-tail keywords in your headings. These more specific phrases can help capture targeted search queries, improving your chances of ranking for a wider variety of relevant searches.
2. Keep the hierarchy
Structure your headings logically, starting with an <H1> for the main topic, followed by <H2> for subtopics, and <H3> for further details. Skipping heading levels can confuse both users and search engines, so ensure each level flows naturally into the next.
3. Align headings with content
Make sure each heading is aligned with the words of that section, so everything makes sense for the reader and assists with higher SEO performance. Writing headings that are not aligned with the content of the section confuses the reader and can cause the search engine to consider your content as not related to the search.
Having clear, informative headings creates an easy pathway so humans and search engines have an easier time both reading and understanding your content, which in turn helps with user retention (although this is a more elusive SEO metric), the overall joy of reading your content, and your SEO rankings.
4. Match search intent
It’s important to understand the search intent that underpins the keyword. Look at why users are searching for those terms in the first place and make sure your headings meet that search intent.
Headings that are user-focused and meet search intent are more likely to keep users engaged and reduce your bounce rate, which should contribute to better organic search rankings. If your content meets what users are searching for, it’s more likely to convert, so optimizing for search intent becomes a crucial part of your SEO strategy.
5. H1 best practices
Your <H1> is the most important heading and should be used only once. It should be concise, engaging, and include your focus keyword.
A well-optimized <H1> sets the tone for both users and search engines, improving engagement and reducing bounce rates by clearly signaling the main topic. Better yet, the right keywords and powerful language used in your <h1> tag can persuade readers to stay on your site and keep them interested. By embracing keywords within the title, you will lessen your chances of people leaving your site too quickly (called a ‘bounce rate’) and increase user engagement.
Common heading tag mistakes
Even a few mistakes with heading tags can hurt your content’s performance. Here are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them to ensure your headings work effectively for your site:
Using H1 tag more than once
While HTML5 allows for multiple <H1> tags, it’s still recommended to stick to one <H1> per page to avoid usability and SEO issues. Overusing <H1> can confuse both users and search engines, disrupting the page’s hierarchy. Reserve the <H1> for the main title, and use lower-level headings like <H2> and <H3> for subtopics.
Skipping heading levels
You should never jump from an <h1> to an <h3> level, it will break the flow of the content. When reading this, it should make sense and look right to the user; the same goes for indexing by search engines: if there is no clear flow you will be ranked lower on SERPs. Additionally, when you skip a level, it can be hard for users to know what the structure of the content is.
Using headings for styling
Jumping from an <H1> to an <H3> breaks the content’s flow and can confuse both users and search engines. The structure should be logical and clear, ensuring smooth navigation and a better reading experience. Skipped levels can lead to lower SERP rankings and make the content harder to follow.
Keyword stuffing
Keyword stuffing is the practice of overloading content with keywords to manipulate search rankings. This makes headings look unnatural and harms readability. If keywords aren’t used naturally, they add little value and can even lead to search engine penalties, defeating the purpose of optimizing for SEO. To avoid this, strike a balance between optimization and readability in your headings.
Ignoring headings for small sections
Failing to use subheadings for smaller sections turns content into a block of text, making it harder to read. Subheadings break up text, improving readability and SEO. They help readers navigate the page, keep engagement high, and reduce bounce rates while making your content more approachable.
How to check HTML headings
Proper use of headings is one of the basic rules of good SEO and content quality. To ensure your heading structure is correct and improve your site audit process, use these tools to keep your content aligned and on point:
Check HTML headings in WordPress
In the Gutenberg block editor, you can view the outline of your headings. When editing the desired page, click on the three vertical dots in the top-right corner of the editor and select “Outline.” This will display a structured list of your headings, helping you ensure they are properly organized and follow the correct hierarchy.
Check html headings using an extension
Another way to check heading tags is by using a browser extension, like the free Web Developer extension. It gives you a clear visual overview of your heading hierarchy, making it easy to spot and fix any errors. The tool also helps you see how search engines might interpret your headings.
Use Similarweb’s Site Audit tool
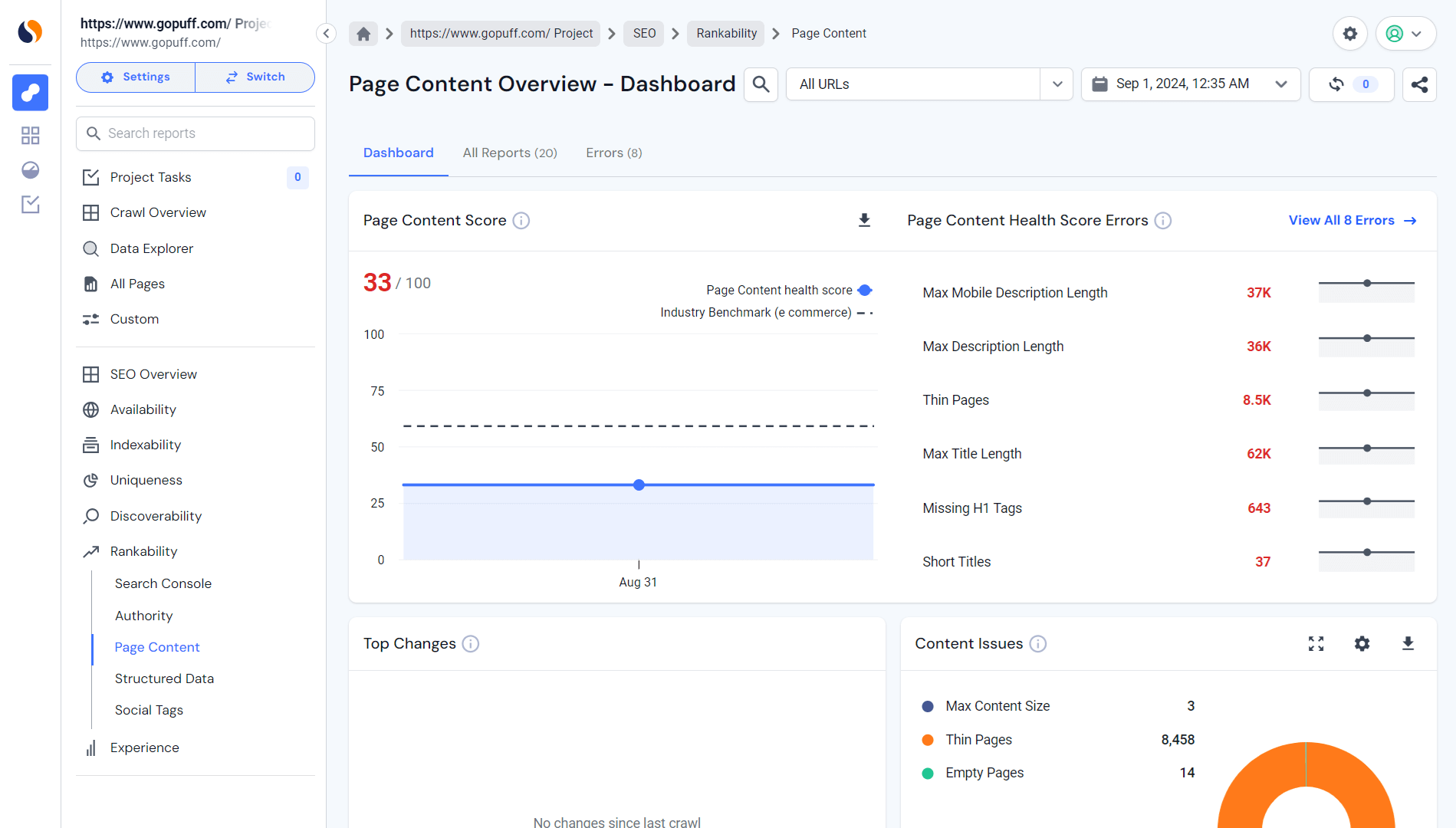
H1 tags audit
You can perform a complete H1 audit of your site using Similarweb’s Site Audit tool. Simply follow these steps: Visit a crawled site, navigate to SEO > Rankability > Page Content.
An H1 audit reviews your heading structure to ensure you meet SEO best practices. It’s recommended to conduct this audit at least once or twice a year for smaller sites, and more frequently for larger ones. The audit will flag any issues with your heading structure, allowing you to fix them and improve your SEO performance.
H2-H6 audit
Detect heading hierarchy issues using our audit tool with a custom extraction. This helps identify problems like <H4> headings following <H2> without an <H3> in between, or <H3> immediately after an <H1>.
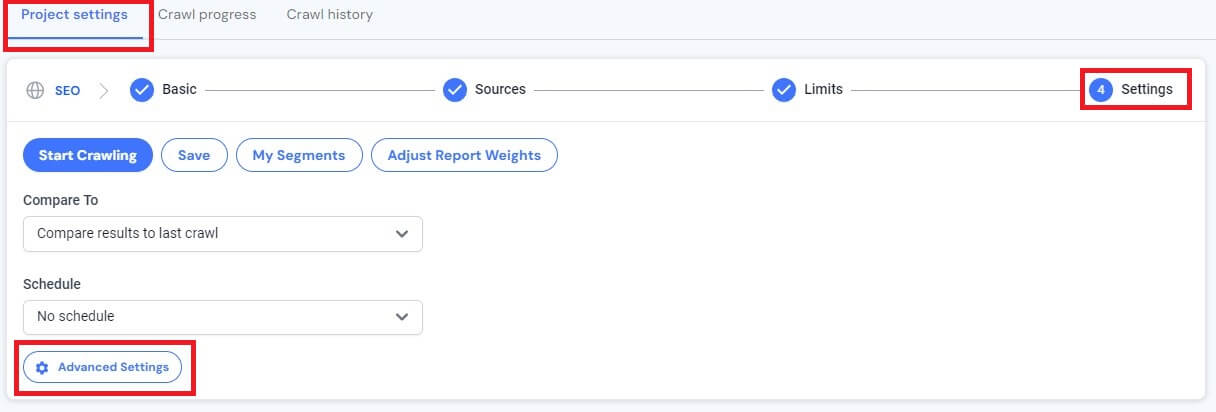
To access, go to Project Settings > Settings > Advanced settings
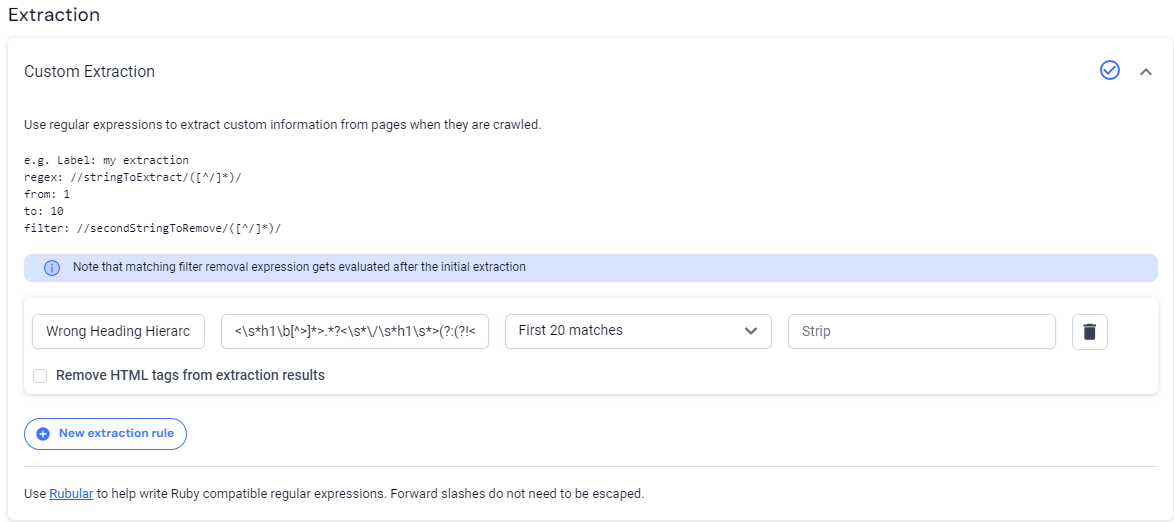
Scroll down to Extractions and under Custom Extractions click New extraction rule and paste this regex:
<\s*h1\b[^>]*>.*?<\s*\/\s*h1\s*>(?:(?!<\s*h2).)*<\s*h[3-6].*?>(.*?)<\s*\/\s*h[3-6]\s*>|<\s*h2\b[^>]*>.*?<\s*\/\s*h2\s*>(?:(?!<\s*h3).)*<\s*h[4-6].*?>(.*?)<\s*\/\s*h[4-6]\s*>|<\s*h3\b[^>]*>.*?<\s*\/\s*h3\s*>(?:(?!<\s*h4).)*<\s*h[5-6].*?>(.*?)<\s*\/\s*h[5-6]\s*>|<\s*h4\b[^>]*>.*?<\s*\/\s*h4\s*>(?:(?!<\s*h5).)*<\s*h6.*?>(.*?)<\s*\/\s*h6\s*>
Name the label however you prefer; we named ours “Wrong Heading Hierarchy.” Then, select “First 20 matches.”
You can access the report via the Custom report or by searching for the label’s name in the search bar. The report will show you the heading with the hierarchy issues.
Effective heading tags: Your new SEO game-changer
Nailing your heading tags is more than just good practice – it’s essential for your SEO. Well-structured headings don’t just help search engines; they guide your readers through your content, making it easier to navigate and more engaging. By following best practices, you’ll enhance both user experience and SEO performance. And with Similarweb’s SEO audit tool, you can track the impact of those optimized headings in real time.
Ready to supercharge your website’s SEO?
The secret to great content and winning at SEO? It’s all about having the right insights at your fingertips. With Similarweb’s Digital Data, you can:
- Perform a competitive site audit to find and fix any SEO issues
- Understand your competitive landscape and perform a keyword gap analysis
- Explore your competitors’ content to spark fresh ideas and uncover new opportunities
- Discover trending keywords and niche topics that will resonate with your audience
FAQs
How many H1 tags should a page have?
Each page should have only one H1 tag, focused on the main topic and including the primary keyword for the best SEO impact.
Can I use CSS for styling headings?
Yes, use CSS for styling, but ensure the heading elements reflect the hierarchical structure of your content.
What are the best practices for subheadings?
Subheadings should follow a logical order (H2, H3, etc.), align with their content, and incorporate relevant keywords to improve SEO.
What’s the ideal number of heading tags per page?
There’s no strict limit – use as many as needed to logically structure your content. Typically, this includes one H1 and several H2 and H3 tags.
Do all heading tags need to include keywords?
Including keywords is helpful, but avoid keyword stuffing. Headings should be optimized but remain natural for balanced, readable content and better SEO.
The #1 keyword research tool
Give it a try or talk to our marketing team — don’t worry, it’s free!