Google Algorithm Updates: Latest News & History

Google’s search algorithm is always changing, leading to fluctuations in search rankings over time. Wrapping up 2025 with Google’s third confirmed core algorithm update and one spam update.
Below is a current overview of both confirmed and unconfirmed updates, along with helpful resources to better understand what changed and how it might affect your site.
The volatility score data is taken from our SERP Seismometer, tracking SERP Volatility in Google.
2025 – Google Updates
December 2025 Core Update
Confirmed update
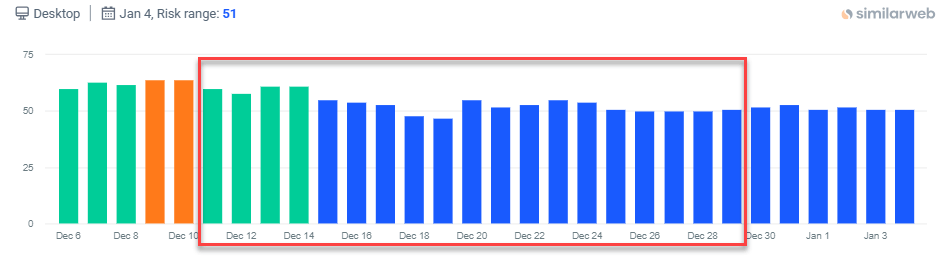
Google launched the December 2025 Core Update on December 11, and the rollout officially completed on December 29, taking just over 18 days. As with all core updates, this was a broad update aimed at improving the relevance and quality of search results across all regions and languages.
Our SERP Seismometer shows some movement ahead of the rollout, with increased activity around December 9–10, followed by steady fluctuations throughout the rollout period. Volatility gradually normalized toward the end of December, indicating that rankings began to settle shortly after the update completed. For full coverage and expert analysis, see Barry Schwartz’s report on Search Engine Land.
August 2025 Spam Update
Confirmed update
Google launched the August 2025 Spam Update on August 26, and the rollout officially completed on September 22 after nearly 27 days. This broad update aimed at improving Google’s spam-detection systems, targeting manipulative tactics such as auto-generated content, cloaking, and link networks.
Our SERP Seismometer shows search results spiked between September 13-15, then quickly settled down, with stability returning by the end of the month. For full coverage and expert analysis, see Barry Schwartz’s report on Search Engine Land.
June 25 Core Update
Confirmed update
Google launched the June 2025 Core Update on June 30, 2025. The rollout lasted 16 days and was officially completed on July 17, 2025. This was the second confirmed core update of the year and turned out to be one of the most impactful. Sites affected by previous Helpful Content and Reviews updates saw some recoveries, based on Search Engine Land. Our tool doesn’t show a meaningful impact after July 18, as indicated in the SERP Seismometer.
March 25 Core Update
Confirmed update
Our tool doesn’t show a meaningful impact since:
2024 – Google Updates
December 24 Spam Update
Confirmed update
On December 19, Google launched the December 2024 Spam Update, and the rollout finished on December 26. This was a general spam update and the third spam update in 2024. Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Land reported on the update on December 26.
Our tool shows an increase since December 22:
December 24 Core Update
Confirmed update
On December 12, Google launched the December 2024 Core Update, and the rollout finished on December 18. As usual, Google updated its core ranking system to improve the search results. Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Land reported on the update on December 18.
Our tool shows a decrease since December 14 and a recovery since December 22:
November 24 Core Update
Confirmed update
On November 11, Google launched the November 2024 Core Update, and the rollout finished on December 5. The update was designed to improve the quality of search results by showing more content that people find genuinely useful.
On December 6, 2024, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on the update. Our tool shows a higher volatility since December 5:

August 24 Core Update
Confirmed update
On August 15, Google launched the August 2024 Core Update. The rollout took 19 days to complete and ended on September 3. Barry Schwartz reported that during the update’s first 4 days, there was a search ranking bug affecting a large number of search results.
Google’s John Muller said that the update is said to show “more content that people find genuinely useful and less content that feels like it was made just to perform well on Search.”
June 2024 Spam Update
Confirmed Update
On June 20-27 Google rolled out a spam update.
Our SERP Seismometer showed SERP volatility. On June 21-June 25: desktop volatility was very high – ranging from 72 to 110. Mobile was more moderate, from 65 to 102. It peaked in the 21st with 110 (desktop) and 102 (mobile)
This was a global update, impacting all regions and languages, meant to detect sites that violate some of Google’s search spam policies. Link spam and site reputation abuse were not targeted.
According to Google, the update rolled out between June 20th to June 27th.
On June 28, Barry Schwartz stated that “This was a broad spam update, not a link spam update, and it did not automate the site reputation abuse policy.”
March 2024 Spam Update
Confirmed Update
On March 20th, Google launched the March 2024 Spam Update, and the rollout finished on March 20th.
The update was made to fight against three types of spam: Expired domain abuse, scaled conteny abuse and site reputation abuse.
On March 20, 2024, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on the update.
March 2024 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On March 5th the SERP Seismometer showed high levels of SERP fluctuations on mobile, reaching 64 on our index. On March 9th, both mobile and desktop rankings reached a high level of volatility, with Desktop ranking fluctuations being higher than mobile and reaching 67.
This update was a more complex update than usual for Google since it contains updates to several components of the overall core system.
According to Google, the update roll-out duration was 45 days. Fluctuation levels were high as multiple updates were launched within it.
As stated by Elizabeth Tucker: “There will be more fluctuations in rankings than with a regular core update, as different systems get fully updated and reinforce each other”
On March 5th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported this announcement and the entire statement.
February 2024 Update
Unconfirmed Update
On February 23rd the SERP Seismometer reported medium-high levels of SERP volatility on desktop only. On February 24th, fluctuation levels measured by our Seismometer reported Earthquake level fluctuations of 79 on Desktop and 75 on Mobile, reaching a record high for the past 90 days.
On February 25th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported volatility levels from several tools as well as industry chatter.
2023 – Google Updates
November 2023 Reviews Update
Confirmed Update
On November 8th & 10th the SERP Seismometer reported medium-high levels of SERP volatility on desktop and mobile. On November 9th, our Seismometer reported surprisingly low fluctuation levels.
On November 8th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter. This update is rolling out in parallel to the November 2nd Core Update.
November 2023 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On November 5th the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on desktop and mobile. On mobile, the fluctuations started on November 4th while desktop volatility was shown on the 5th.
On November 3rd, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter. He also speculated that the update might be related to the recent “bug with the October 2023 core update”.
October 2023 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On Oct. 5th, Google launched the September 2023 Core Update, and the rollout finished on Oct. 19th. This update was made in tandem with the October 2023 Spam Update.
On Oct. 20, 2023, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on the update.
October 2023 Spam Update
Confirmed Update
On Oct. 4th, Google launched the October 2023 Spam Update, and the rollout finished on Oct. 20th.
The update was made to fight against four types of spam: cloaking, hacked content, auto-generated content, and scraped content spam.
On Oct. 20, 2023, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on the update.
September 2023 Helpful Content Update
Confirmed Update
On Sep. 14th, Google launched the September 2023 Helpful Content Update, and the rollout finished on Sep. 28th.
This update was meant to help promote helpful content and demote unhelpful content. This is not according to Google considered a Core Update.
On Sep. 28, 2023, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on the update.
August 2023 Broad Core Update
Confirmed Update
On August 22, 2023, Google announced that the August 2023 Broad Core Update had been released. Google said the rollout may take up to two weeks to complete.
The SERP Seismometer reported a high level of fluctuation a few days later on August 25, 2023.
On Aug. 23, 2023, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported Google’s announcement.
August 3-4 2023 Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On August 3rd, the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. Fluctuations returned to normal on August 4th, however, there were reports of fluctuations as well on August 4th.
On August 4th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
July 12th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On July 12th, the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on desktop and mobile. On July 13th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
June 14th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On June 13th the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on desktop. On mobile the fluctuations started on June 7th.
On June 14th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about the fluctuations including industry chatter. On June 19th he reported on continuing fluctuations commenting that he had not seen a period of fluctuations this long with such heated volatility without a confirmed update..
June 6th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On June 6th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported elevated SERP fluctuations and a spike in industry chatter. He also speculated that the fluctuations might be related to the recent Spam Update.
Google I/O Search Algorithm Update
Unconfirmed Update
Although the SERP Seismometer had been reporting high levels of rank fluctuations, on May 12th Barry Schwartz reported high levels of industry chatter. He observed that the update seems to have started on May 10th which is the same day that Google I/O kicked off.
May 17th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On May 16th the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on desktop and mobile.
On May 18th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter. A portion of that chatter commented how their rankings seem to have reverted from earlier updates.
May 1st & 2nd Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On April 20th the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on both desktop and mobile search results. The fluctuations continued the following days.
On May 3rd, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
The April 2023 Reviews Update
Confirmed Update
On April 12th, Google announced that the April 2023 Reviews update had been released.
This update included reviews about products, services, and things and as a result, Google changed the name from ‘Product Reviews Update’ to just ‘Reviews Update’.
The SERP Seismometer did not report elevated levels of SERP fluctuations.
On April 13, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported Google’s announcement, its nature, and limited industry chatter.
Google March 2023 Broad Core Update
Confirmed Update
On March 15th Google announced on Twitter that the March 2023 Broad Core Update was live. The next day, the SERP Seismometer reported a massive spike in SERP fluctuations on both mobile and desktop.
On March 16, Barry Schwartz or Search Engine Roundtable reported on industry chatter.
Ongoing SERP Fluctuations
Unconfirmed Update
Following the announcement of the Product Reviews update, on February 22nd the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on desktop and mobile. The high levels of fluctuations continued to March 5th peaking on February 25th and March 1st.
On March 6th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about the ongoing fluctuations.
The February 2023 Product Reviews Update
Confirmed Update
On February 21st, Google announced that the February 2023 Product Reviews update had been released.
On February 22nd, the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on both desktop.
On February 22, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported Google’s announcement, its nature, and limited industry chatter.
February 14th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On February 14th, the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of fluctuations on mobile. The fluctuations grew over the next few days expanding to include desktop.
On February 15th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
February 8th/9th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On February 9th the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. Fluctuations peaked the next day on the 10th and returned to normal levels on the 13th.
On February 10th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
February 4th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On February 4th the SERP Seismometer reported a massive spike in SERP fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. The fluctuations returned to normal levels the following day.
On February 6th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported the high levels of fluctuations as well as industry chatter.
January 26th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On January 26th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported a potential unconfirmed Google update that happened on January 26th.
Although the SERP Seismometer didn’t report high levels of SERP fluctuations, Glenn Gabe shared screenshots of sites previously impacted by updates that were seeing big swings in their traffic.
January 18th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On January 18th the SERP Seismometer reported a slight increase in SERP fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. The fluctuations returned to normal on January 21st.
On January 19th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
January 14th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On January 14th, the SERP Seismometer reported a spike in SERP fluctuations on desktop. Fluctuations returned to normal the following day.
On January 16th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
January 11th Unconfirmed Update
Confirmed Update
On January 11th the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on mobile. On the same day, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported that the fluctuations were accompanied by industry chatter.
He noted that it’s not clear if the fluctuations were caused by an unconfirmed update or were a result of the December 2022 Link Spam or Helpful Content update.
2022 – Google Updates
December 2022 Link Spam Update
Confirmed Update
On December 14th Google announced that the December 2022 Link Spam update began rolling out. According to their announcement, Google is using a machine learning algorithm called SpamBrain to neutralize the impact of unnatural links on search results.
On December 14th, the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on both mobile and desktop, and the fluctuations continued for the next few days.
On December 15th, Barry Schwartz or Search Engine Roundtable explained what the update is designed to do. He also reported on industry chatter.
December 22 Helpful Content Update
Confirmed Update
Google announced on Twitter that the December 2022 Helpful Content update began rolling out on December 5th.
On December 5th the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on both mobile and desktop. Fluctuations increased over the next few days massively spiking on December 8th.
On December 7th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on industry chatter.
November 30th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On November 22nd the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. The fluctuations continued the following days and peaked on November 30th. Fluctuations returned to normal on December 4th.
On December 5th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
November 18th – 20th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On November 18th the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. Although the fluctuation levels on desktop returned to normal the following day, fluctuations continued on mobile.
On November 21st, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
October 28th Unconfirmed Update / Adjustment
Unconfirmed Update
On October 28th the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on mobile. SERP fluctuation levels returned to normal the following day.
On November 1st, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter. He mentioned that some SEOs were noticing that sites hit by previous updates were seeing big swings in terms of their Google rankings and traffic.
October 22nd Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On October 22nd the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of SERP fluctuations on desktop. On mobile the fluctuations started on October 21st. SERP fluctuation levels returned to normal on October 23rd on both mobile and desktop.
On October 24th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter. He also speculated that the fluctuations might be related to the recent Spam Update.
October 2022 Spam Update
Confirmed Update
On October 19th, Google announced on Twitter that the October 2022 Spam Updated had been released.
On October 20th, Barry Schwartz or Search Engine Roundtable reported limited industry chatter and ranking fluctuation.
September 2022 Product Reviews Update
Confirmed Update
On September 20th, Google announced on Twitter that the September 2022 Product Reviews update had been released.
On September 22, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on industry chatter.
September 2022 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On September 12th Google announced that the September 2022 Core Updated had been released.
The next day, the SERP Seismometer reported a massive increase in SERP fluctuations on both mobile and desktop.
On September 13th Barry Schwartz or Search Engine Roundtable reported on industry chatter.
Helpful Content Update Fluctuations
Unconfirmed Update
On September 8th the SERP Seismometer reported a spike in SERP features on both mobile and desktop. The fluctuations peaked the next day and returned to normal on September 10th.
It’s interesting to note that these fluctuations happened at the tail end of the Helpful Content Update rollout. What’s also interesting is that the fluctuations ended on the day that Google announced that the update was completed.
On September 9th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable speculated that the fluctuations were related to the update. He also reported on industry chatter.
Helpful Content Update
Confirmed Update
On August 25th, Google confirmed on Twitter that the Helpful Content update was live.
Google pre-announced the update on its blog explaining that the update was designed to weed out low-quality content.
It’s interesting to note that on the day the update went live, the SERP Seismometer reported normal levels of SERP fluctuations on both mobile and desktop.
On August 25th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported that the update was live
August 9th Outage
Unconfirmed Update
On August 9th, Google suffered a massive outage that caused:
Indexing issues
Pages dropping out of Google’s index
Low-quality outdated search results
The outage was apparently caused by a fire in one of Google’s data centers.
The outage caused massive SERP fluctuations which were picked up on the SERP Seismometer on August 9th and 10th on both desktop and mobile. SERP fluctuations returned to normal on August 11th.
On August 9th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported the incident.
July 2022 Product Reviews Update
Confirmed Update
On July 27th, Google announced on Twitter that the July 2022 Product Reviews update was released.
It’s interesting to note that on July 27th the SERP Seismometer reported normal levels of SERP fluctuations on both mobile and desktop.
On July 28th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported minimal levels of industry chatter.
June 2022 Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On June 20th the SERP Seismometer began tracking high levels of SERP fluctuations on both mobile and desktop. The tremors began increasing during the following days.
On June 21st, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported high levels of industry chatter. He also commented on how search fluctuations occurred both before and after the May Core update.
Google May 2022 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On May 25th 2022, Google announced that the May 2022 Core update was live. The following day on May 26th, the SERP Seismometer reported a huge spike in rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. Although fluctuation levels returned to normal the next day, a core update typically takes two weeks to roll out completely.
On May 26th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on the update commenting on high levels of industry chatter.
May 16th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On May 16th, the SERP Seismometer tracked a moderate increase in SERP fluctuations. On mobile the fluctuations continued for a few days finally returning to normal on May 20th. On Desktop the fluctuations returned to normal on May 18th.
On May 17th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported high levels of industry chatter.
Mother’s Day Weekend Search Algorithm Update
Unconfirmed Update
On May 7th, the SERP Seismometer reported high levels of rank fluctuations on mobile. The following day on May 8th, rank fluctuations spiked dramatically on both mobile and desktop. Fluctuations gradually decreased over the next few days returning to normal by May 13th.
On May 8th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on significant industry chatter.
March 2022 Product Reviews Update
Confirmed Update
On March 23, Google announced on their blog that the March 2022 Product Reviews Update went live. Two days later on March 25th, the SERP Seismometer reported a small spike in SERP fluctuations. The fluctuations decreased the next day.
On Mar 24th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported what the focus of the update was and what it included. He also mentioned low levels of rank fluctuations and industry chatter.
Spring 2022 Google Search Ranking Algorithm Update
Unconfirmed Update
On March 18th the SERP Seismometer reported a small increase in SERP fluctuations on both mobile and desktop. The fluctuations increased reaching a peak on March 20th and slowly decreased over the next few days.
On March 20th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported large amounts of industry chatter.
March 4th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On March 4th the SERP Seismometer reported a spike in rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. The fluctuations died down the next day.
On March 6th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter.
January 22nd Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On January 22nd the SERP Seismometer reported high rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. The fluctuations peaked substantially the next day and fluctuations returned to normal on January 24th.
On January 23rd, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about industry chatter.
January 14th and 15th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On January 14th the SERP Seismometer reported moderate levels of rank fluctuations which were followed by a massive spike in fluctuations the next day on both mobile and desktop. The fluctuations returned to moderate levels on January 16th and died down the next day.
On January 17th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported moderate amounts of industry chatter.
January 12th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On January 12th the SERP Seismometer reported moderate rank fluctuations primarily on desktop. The fluctuations returned to normal the next day.
On January 12th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on industry chatter.
2021 – Google Updates
December 2021 Product Reviews Update
Confirmed Update
On December 1st, Google announced on the official blog that the December 2021 Product Review update had begun rolling out.
The SERP Seismometer showed a spike in SERP fluctuations on both desktop and mobile on December 2nd. High levels of fluctuations continued to December 7th and returned to normal on December 8th.
On December 5th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about the high levels of fluctuations as well as industry chatter.
November 2021 Core Update
Confirmed Update
Google announced on November 17th, that they were to be releasing the November Core Update that day. On November 18th the SERP Seismometer reported a spike in SERP fluctuations both on mobile and desktop. The fluctuations reverted back to normal levels the next day.
Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported industry chatter on November 18th.
November 2021 Spam Update
Confirmed Update
Starting on November 3rd, the SERP Seismometer tracked a moderate jump in fluctuations on both desktop and mobile.
The next day, Google announced on Twitter that a spam update had been released.
On November 4th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported limited industry chatter.
October 2nd and 3rd Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On October 2nd and 3rd, the SERP Seismometer reported a large spike in rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile.
On October 4th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about limited industry chatter.
September 24th and 25th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On September 24th the SERP Seismometer reported a large spike in rank fluctuations which were still active on the 25th. They returned to normal on September 26th.
On September 27th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about industry chatter.
August 15th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On August 13th the SERP Seismometer picked up massive fluctuations on both mobile and desktop which continued the following day.
On August 15th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about industry chatter.
Link Spam Update
Confirmed Update
On July 26th, Google announced that they began rolling out the Link Spam update. The update is designed to broadly identify and nullify spam across multiple languages.
The SERP Seismometer only reported an increase in fluctuations on the 29th which disappeared the next day.
On July 27th and July 29th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported limited industry chatter.
July 2021 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On July 1st, Google announced on Twitter that the July 2021 Core Update had been released. This was the second part in a two-part core update that was originally announced on Twitter on June 2nd.
A day later, the SERP Seismometer reported dramatic fluctuations on both desktop and mobile which died down the next day.
On July 2nd, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about the unique nature of the update, as well as industry chatter.
Google Spam Update – Part Two
Confirmed Update
On June 28th, Google announced on Twitter, that they had released part two of the spam update. Google also confirmed that the update took one day to complete.
The SERP Seismometer did not report any unusual ranking fluctuations.
On Jun 29th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported that the update went live. He also reported a low level of industry chatter.
June 23rd Spam Update
Confirmed Update
Starting on June 23rd, the SERP Seismometer tracked moderate fluctuations on both desktop and mobile.
On the same day, Google announced on Twitter that a spam update had been released and confirmed that it was completed that day.
On June 24th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported a small amount of industry chatter.
Google Page Experience Update
Confirmed Update
On June 15th, Google announced on Twitter that the Page Experience update begun slowly rolling out. Google stated in the tweet that the update would be completed by the end of August.
In keeping with the slow nature of the update, the SERP Seismometer showed a record low level of fluctuations on the 15th.
On June 16th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported that the update went live.
June 2021 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On June 3rd, Google announced on Twitter that the June 2021 Core Update was released. A day later, the SERP Seismometer reported dramatic fluctuations which lasted until June 6th.
On June 7th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on unusually low levels of industry chatter.
May 22nd Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On May 20th SERP Seismometer reported a spike in fluctuations. The following day, there was a decrease in fluctuations, but fluctuations resumed on May 22nd. The fluctuations stopped on May 24th.
On May 23rd Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported massive fluctuations that occurred on May 22nd and noted that the industry chatter did not match the levels of fluctuations.
April 30th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On April 30th the SERP Seismometer reported a large spike in rank fluctuations. The fluctuations peaked the next day and fluctuations returned to normal on May 2nd.
On May 3rd, while reporting industry chatter, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable speculated that the update had an impact on the Product Reviews Update.
April 23rd Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On April 23rd, the SERP Seismometer began tracking a moderate increase in rank fluctuations which carried through to the 24th. The update affected both global web search results and local search results.
On April 26th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about industry chatter.
Product Review Update
Confirmed Update
On April 8th Google announced the launching of the Product Review update which is specifically focused on product review content.
Starting on April 9th, the SERP Seismometer reported a massive spike in ranking fluctuations both on mobile and desktop. The volatility carried through to April 11th and settled by April 12th on desktop. On mobile, the fluctuations carried through to April 13th.
Fluctuations resumed on April 15th and died down on April 18th on both Desktop and mobile.
Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on the update on April 9th.
March 10th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On March 10th, the SERP Seismometer reported an increase in Google SERP fluctuations on both mobile and desktop. The fluctuations peaked on March 13th and concluded on March 14th on desktop and March 15th on mobile.
On March 11th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported an increase in industry chatter.
February 17th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On February 17th the SERP Seismometer reported a large spike in rank fluctuations. The spike occurred after a series of minor fluctuations that followed the Passage Ranking update. Due to its proximity to the Passage Ranking update, this could simply be a set of fixes designed to support the findings after the Passage Ranking update.
On February 17th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported about industry chatter.
Passage Ranking Update
Confirmed Update
Starting on February 9th, the SERP Seismometer began tracking a massive spike in rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile that carried over to February 10th. Google confirmed on Twitter that Passage Ranking went live on February 10th for queries in the US in English.
On February 12th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported that Passage Ranking went live in the US and that surprisingly chatter was low after February 10th.
2020 – Google Updates
December 18th Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On December 17th, just a day after Google announced on Twitter that the December 2020 Core Update rollout was complete, the SERP Seismometer began tracking a small increase in rank fluctuations which peaked on December the 18th.
December 2020 Core Update
Confirmed Update
Starting on December 1st the SERP Seismometer began tracking an increase in rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. This carried on until December 4th where there was a massive spike in SERP volatility. Fluctuations returned to normal on December 5th.
On December 3rd, Google announced that there would be a core update later that day. The announcement corresponds with the sudden spike in fluctuations that happened on December 4th.
Also on December 4th Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on industry chatter aligned with the updates recorded by the SERP Seismometer.
September 16th 2020 Update
Unconfirmed Update
On September 15th, the SERP Seismometer reported an increase of rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. The fluctuations peaked on September 16th reaching an earthquake risk level of 104. The fluctuations steadily decreased from that time on, reaching normal levels on September 21st.
On September 17th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on industry chatter.
August 15th 2020 Update
Unconfirmed Update
On August 15th, the SERP Seismometer reported a dramatic increase in rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. Fluctuations reached an unprecedented earthquake risk level of 130 on August 15th and 119 on August 16th. By the time the update was complete, the dramatic rank changes were generally reverted.
On August 15th, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported on significant industry chatter.
June 2020 Update
Unconfirmed Update
Starting on June 9th, the SERP Seismometer began tracking an increase in rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. The fluctuations peaked on June 10th, reaching an earthquake risk level of 83. After four days of elevated fluctuations, levels returned to normal on Jun 13th. However, after three days of normal fluctuation levels, the increased movement returned on June 16th. During the update’s second wave, our seismometer recorded two notable spikes in fluctuations. First, on June 20th the seismometer recorded fluctuations hitting 109, and on June 23rd fluctuations reached 103.
On June 10th, and June 23rd Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Round Table reported on significant industry chatter aligned with the updates recorded by the SERP Seismometer.
May 2020 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On May 4th, 2020, Google’s Danny Sullivan announced that the search engine had started to roll out its second core algorithm update of the year.
Dubbed the May 2020 Core Update, the bulk of the release spanned just two days with the initial roll-out being tempered. As shown on our SERP Seismometer, the second day of the update’s roll-out produced far more rank volatility than first day of the update.
Per our data analysis, the update was unique in that it produced a rather uniform amount of rank volatility across all niches.
May 2020 Core Update Data
Further, the update was large in scope and size as the levels of rank volatility slightly edged out the January 2020 Core Update which was known for its large impact on the SERP.
COVID-19 Algorithm Update
Unconfirmed Update
On March 17th, our SERP Seismometer began recording an unprecedented series of heightened rank fluctuations that lasted into early April. During this time there were 12 days of heightened rank fluctuation levels recorded. Outside of the core algorithm updates, such an extended period of increased fluctuations has not occurred within the past two years, if not more.
The timing of the increases seems to correlate to COVID-19 becoming an official pandemic. In fact, our research indicates that on March 11th, the day that COVID-19 was labeled a pandemic by the WHO, Google made significant ranking changes to COVID-19-related keywords. Further, there was a clear and noticeable pattern vis-a-vis “COVID-19 keywords” that paralleled the various updates during this period. The same pattern was not evident within other keywords subsets.
Search Engine Land hosted a panel of experts on the issue of COVID-19’s impact on search behavior and potential affect this may have had on Google’s algorithm. As our own Mordy Oberstein noted during the panel, “[COVID-19] is a developing story that Google has not really seen before and it keeps spreading in all sorts of directions… and because Google is so good at making connections it (COVID-19) impacts so many different areas…. Google is trying to figure out how far does COVID-19 reach and how accurate are we (i.e., Google) based upon what’s going on.”
Rank Reversal Pervasive in February Update
Unconfirmed Update
On February 8th, the SERP Seismometer began recording significant increases in rank fluctuations that lasted for a total of six days. At their peak, the fluctuation increases hit a level of 94/120.
Along with the increases tracked by our SERP weather tool, a significant amount of industry chatter pointing to a powerful update was reported by Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable.
An initial investigation into the update showed numerous “reversal patterns.” To that, many sites who were hit by the update initially saw a quick return to normal while some sites hit by the January 2020 Core Update underwent a reversal.
Featured Snippet URL Duplication Removed From Organic Results.
January 22nd – Confirmed Update
On January 22nd, Google Search Liaison, Danny Sullivan, announced a major divergence from Google’s longstanding Featured Snippet practices. Traditionally, Google has shown the URL used within a Featured Snippet among the top organic results as well as a part of the Featured Snippet itself. Per Sullivan’s announcement, the only time the URL used inside a Featured Snippet will be shown on page one of the SERP is in the Featured Snippet box. Google is no longer duplicating Featured Snippet URLs among the page one organic results. Such URLs, however, may appear on pages beyond page one.
Along with the change, Google has also announced that the Explore Panel, a hybrid between a Featured Snippet and a Knowledge Panel, will start to appear within the SERP’s main column, not to the right of the results as they were placed previously. This change specifically addresses concerns from within the SEO industry that the CTR of Explore Panel links will dwindle with the removal of said links from the organic results.
These alterations to the SERP have resulted in the industry considering Featured Snippets to be “position 1” and no longer “position 0.” Such a construct has far-reaching consequences, among them how to properly track rank for the top position on the Google SERP.
January 2020 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On January 14th, and per Google’s advanced notice, the January 2020 Core Update began to roll-out. The initial levels of rank fluctuations caught on the SERP Seismometer presented extreme levels of rank volatility on both desktop and mobile.
As the update continued to roll-out over the coming days, rank slowly began to stabilize before finally returning to normal levels on January 19th.
Per a data analysis, and consistent with almost all other core updates to this point, Your Money Your Life niches were significantly impacted, more so than other industries (as can be seen in the below graph):
Jan 2020 Core Update Data
Read our full analysis for more data on the January 2020 Core Update.
2019 – Google Updates
The November 2019 Local Update
Confirmed Update
On December 2, 2019 Google’s Danny Sullivan confirmed what the search community had already suspected, the roll-out of a local algorithm update. Officially named the November 2019 Local Update, Sullivan indicated that the update began rolling out in early November 2019.
In specific, the November 2019 Local Update introduced neural matching to the local algorithm. As a result, businesses with titles and descriptions that vaguely related to a vertical may now appear within the top organic results as well as within the Local Pack.
Google Implements BERT Algorithm
Confirmed Update
On October 25th, Google announced that it had begun to implement its BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) algorithm. Per Google, BERT is said to impact 10% of all queries and is the search engine’s “biggest leap forward in the past five years.”
The algorithm was birthed out of an open-sourced project aimed at using neural networks to advance contextual understanding of content via natural language processing (NLP).
In simple terms, BERT is meant to help better interpret a query by using a contextual understanding of the phraseology employed. This is done as the entire phrase is analyzed at once which lets BERT understand a keyword term according to all of the words used within it. This stands in contrast to models that look at language from left-to-right thereby pinning a word’s understanding to that which preceded it.
Practically speaking, BERT helps Google to better understand the use of prepositions within a search query as well as to better comprehend words that have double meanings by using contextual understanding.
Note, there were not large waves of rank fluctuation increases due to BERT’s roll-out.
September 2019 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On September 25th, Google rolled-out it’s third core algorithm update of 2019. Dubbed the September 2019 Core Update by Google’s Danny Sullivan, the update was a significant ranking event.
As shown on the SERP Seismometer the update rolled out over the course of two days with rank fluctuation levels reaching a high of 79 on desktop (78 on mobile).
Both the length and level of fluctuations recorded by the seismometer were on the “low side” in comparison to previous core updates. This is evidenced when comparing the rank volatility increases of the September update to the June 2019 Core Update.
September 2019 Review Rich Results Update
Confirmed Update
On September 16th, 2019, Google made a significant update to its practice of showing reviews within organic results. Per the update, Google no longer allows what it calls “self-serving reviews” to appear on the SERP. This means that sites can no longer use schema markup to place reviews shown on its own website within rich results on the SERP. This applies even to reviews placed on the brand’s site via a third-party integration.
As a result, our SERP Feature Tracker indicates a 5 point drop in the number of page one SERPs that contain a review within the organic results.
Google also indicated that the ‘name’ property must be indicated within the structured data. That is, you must name the product being reviewed.
Lastly, Google released a list of the schema formats that are eligible to produce a review within a rich result.
[You can use our Schema Markup Generator to easily create the code that produces rich results.]
Original Reporting Preference
Confirmed Update
On September 12th, Google officially announced it had updated its algorithm so that original reporting would receive ranking preference. To this effect, Google has said that it is now better at determining the original source of news reporting. As a consequence of this, the search engine is more proficient at ranking the original source of new reporting more prominently on the SERP.
Note, the algorithm was not updated on September 12th itself. Google indicated that it had been implementing and improving on the adjustment throughout the months leading up to the official announcement.
July 2019 Major Update
Unconfirmed Update
On July 18th, the SERP Seismometer tracked extremely high levels of rank fluctuations, recording a peak rank fluctuation level of 113. In doing so, the seismometer presented us with one of the largest ranking earthquakes in years.
The update began on July 16th with moderate levels of rank fluctuations being recorded. Those levels jumped slightly on the 17th before reaching an extremely unusual high on July 18th.
The increases shown on the SERP Seismometer coincided with industry chatter that indicated a “massive” amount of rank movement, as was reported by Barry Schwartz on SERoundtable.
An initial look at the data shows that no one niche type was impacted more than another. Unlike some of Google’s confirmed core updates, Your Money Your Life sites (YMYL) were not impacted by the update any more than other site types.
The June 2019 Core Update
Confirmed Update
On Sunday, June 2nd, 2019, in what was an industry first, Google’s Danny Sullivan took to Twitter to announce a pending core algorithm update. As part of his message, Sullivan indicated that on June 3rd a broad core algorithm update would begin its roll-out.
Notably, Sullivan also announced that the official name of the update would be the ‘June 2019 Core Update’. His doing so was most likely a result of the confusion surrounding the naming of the March 2019 Core Update.
Accordingly, the SERP Seismometer began displaying significantly high levels of rank fluctuations on June 4th (showing a fluctuation level of 91/100).
That said, by June 5th the seismometer indicated that the update’s roll-out was starting to slow slightly as the level of rank fluctuations dropped to 74.
12 March 2019 Core Update
Confirmed Update
Exactly one year after confirming the first of its official “core updates” Google released yet another broad change to its algorithm.
Initially picked up by Rank Ranger’s SERP Seismometer on March 12th, the update was not confirmed by Google until the 13th. That said, the update continued to roll-out even after Google’s confirmation.
Rank changes reached a high on the 13th with the seismometer recording a rank fluctuation level of 89/100 on the desktop SERP.
It should be noted that while Google confirmed the update, it did not name it. As a result, the update has been referred to by multiple aliases per Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable. The two most common names are the Florida 2 Update and the Google 3/12 Broad Core Update.
Major February Rank Fluctuations Spike
Unconfirmed Update
Starting on February 21st, the SERP Seismometer began tracking a prolonged series of increased rank fluctuations. The spike in fluctuations was initially on the more moderate side with fluctuation levels reaching 71/100 on February 22nd.
However, as time progressed, and despite a one day lull in the increased activity (see February 25th), significantly larger fluctuations spikes were observed. Specifically, on February 27th and March 2nd the seismometer recorded unusually elevated fluctuation levels of 91/100 and 86/100 respectively.
2018 – Google Updates
December’s Intent Recalibration
Unconfirmed Update
December 13th saw the SERP Seismometer pick up what became a 6-day increase in rank fluctuations. This prolonged series of heightened rank movement reached a pinnacle on December 16th as the seismometer hit a fluctuation level of 80/100.
On December 17th, Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable posted that industry chatter indicated that sites were significantly impacted by the update.
An early investigation, per our various data-sets, would indicate that the update may have represented a recalibration of how Google understands intent for a wide range of keywords.
Impactful Mid-October Update
Unconfirmed Update
On October 16th the SERP Seismometer reported a surge in rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. The algorithmic event lasted for two days before fluctuation levels returned to normal on October 18th.
The update considerably impacted rank as the tool posted an earthquake risk level score of 81/100 on the 16th.
The SEO community’s forum chatter mirrored the fluctuation levels reported by the SERP Seismometer, as noted by Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable.com.
Minor Confirmed Update
Confirmed Update
On September 27th there was a small amount of industry chatter indicating that Google was tweaking its algorithm. Uncharacteristically, Google, two days after the aforementioned chatter, confirmed that a “small” algorithm update was undertaken.
The confirmation took place on Twitter where Googler Danny Sullivan (using his personal Twitter account) indicated to his longtime colleague Barry Schwartz that indeed there was an update, but it was not “major.”
Interestingly, the SERP Seismometer did show increased fluctuations relative to the extremely low levels of rank changes seen during the days prior to the 27th. The seismometer did record moderately high levels of rank fluctuations on the 29th, the very day Google made its official announcement.
Broad Core Update – August 2018
Confirmed Update
Immediately following early industry chatter, Google confirmed yet another broad core update. This is the third such update of 2018. As with both the March and April broad core updates, Google has advised the SEO community that traffic lose does not indicate poor page quality and it may be the case that there is no “fix.”
It is possible that Google’s explanation points towards the machine learning elements of the algorithm recalibrating their understanding of intent. Such an explanation would explain why there is no fix, why a rank loss is not indicative of poor quality, and why Google has previously said these updates reward previously “under-rewarded” sites. We’ve reached out to Google regarding this but have yet to hear back.
In accordance with the update, the SERP Seismometer is showing an increase in rank fluctuations. During the update, fluctuations have been particularly high as the seismometer shows a volatility level of 92/100 on August 2nd.
Speed Update Released (Mobile)
Confirmed Update
As of July 9, 2018, and good to their word, Google began releasing what has become known as the Speed Update. The update, which was first announced in January 2018, is meant to urge sites to improve mobile page speed. Until now, speed was only a factor on desktop.
Despite initial concerns surrounding the update, Google has reassured site owners that the Speed Update is applicable only to those sites that are considered to be exceedingly slow. Accordingly, minor tweaks to increase page speed will not produce higher rankings according to Google.
At the same time, the update is not zero-sum. That is, as a site improves page speed incrementally, Google will be able to discern the difference in speed. This stands in contradistinction to speed as a desktop ranking factor, which more monolithically determined if a site was too slow and was to be impacted in the rankings accordingly.
The April 2018 Broad Core Update
Confirmed Update
On April 13th, the SERP Seismometer began picking up on what would become a 10-day update to Google’s core algorithm. Ending on April 22nd, the seismometer caught moderate increases in fluctuation levels to the exclusion of April 18th, where a fluctuation level of 75 was recorded.
Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable indicated that chatter among the SEO industry forums had picked up in line with the data being reported by the SERP Seismometer.
For the second consecutive time (see the mid-March core update), Google confirmed the rollout on April 20th, noting that a “broad core algorithm update” was released. Even with the announcement, the specific details surrounding the exact nature of the update remains unclear.
Core Update: March 2018
Confirmed Update
On March 3rd, the SERP Seismometer began recording increased rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. While the uptick in rank fluctuations was initially moderate, the seismometer caught an unusual and highly significant upsurge on March 9th. According to the seismometer, fluctuations reached a level of 99 (out of 100) on desktop and 92 on mobile – That’s an earthquake, people. Over the following days the fluctuations, though still high, tapered off to an extent.
On March 12th, Search Engine Land reported that Google, uncharacteristically, confirmed the update as being related to its core algorithm (thereby explaining the unusually high fluctuations levels of March 9th).
Extended January 2018 Update
Unconfirmed Update
On January 10th the SERP Seismometer began showing increased rank fluctuations on both mobile and desktop. Lasting for an excessive period, the seismometer has tracked anything from moderate to extreme fluctuations. To this extent, on January 21st, the desktop seismometer showed a fluctuation level of 83 out of 100, which is abnormally high.
The mobile seismometer all but paralleled the fluctuations seen on desktop with a few slight variations. In this instance, the fluctuation levels on the 21st reached 85, as opposed to 83 as seen on desktop.
The uptick in fluctuations was picked up by the industry when on January 16th Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable reported on the update.
Google has not confirmed any increase in algorithmic activity.
Page Speed to Become Mobile Ranking Factor
Page Speed – Confirmed Update
On January 17th Google announced that page speed will become a mobile ranking factor. Page speed has been a ranking factor on desktop since 2010. However, with this announcement, the ranking factor will now be an official part of a mobile page’s placement on the Google SERP come July 2018.
According to Google’s announcement, the pending update will target excessively slow loading pages. As such, the search engine does not predict that an extensive number of pages will be impacted as the ranking factor becomes incorporated into the algorithm this July.
The “Speed Update,” as Google is calling it, has brought up questions as to how a mobile AMP page will be impacted by the pending ranking factor. One concern of note revolved around a site using fast loading AMP URLs with the canonical URLs being considerably slow. In such a case, which URL will Google measure the speed of (i.e., the fast loading AMP URL or the slower mobile URL)? Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable reported that in such a case Google had informed him that page speed will be measured according to the AMP URL.
Also of note, according to Google, the pending mobile page speed ranking factor exists independently of the mobile-first index, though what that means exactly is still to be determined.
SearchEngineLand has published a comprehensive mobile page speed as ranking factor FAQ as well.
2017 – Google Updates
Maccabee Update
Unconfirmed Update
On December 20th, the SERP Seismometer tracked a significant increase in rank fluctuations. The update was a one day algorithmic event on desktop, where fluctuation levels went as high as 71 on the scale. Mobile saw a two day roll-out that began on the 19th with moderate increases in fluctuation levels. However, on the 20th, those levels rose significantly on mobile as a fluctuation level of 75 was recorded on the seismometer .
This came on the heels of industry chatter that there was an update a few days prior to the one tracked on the 20th. Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable dubbed the December update, the Maccabee update. Google confirmed that they did release “several minor improvements during this time frame.”
Mid-November Significant Google Update
Unconfirmed Update
On November 14th the desktop SERP Seismometer started tracking increased rank fluctuations. By November 15th the fluctuations had risen to very high levels with the seismometer indicating a fluctuation level of 76.
The fluctuations on mobile were of a similar nature. However, as opposed to desktop, the SERP Seismometer for mobile began tracking elevated fluctuation levels a day earlier, on November 13th. By November 15th the mobile earthquake risk level reached 71, indicating that the fluctuations had increased significantly.
Industry chatter also confirms the roll-out of a substantial Google update. On November 15th, Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable reported that webmasters and SEOs were experiencing noticeable changes in their rankings. Schwartz also speculated that the update does not appear to be related to either Penguin or Panda.
To date, and quite predictably, Google has not commented on the update.
Google ccTLDs No Longer Give Access to International Search Results
Confirmed Update
On October 27th, 2017 Google announced that utilizing a Google country code top-level domain (ccTLD), i.e., google.co.uk, google.ca, etc., will no longer allow users to access international search results. Google indicated that the change comes as part of an effort to deliver more local and thereby relevant results to users. However, the change in ccTLD policy has precipitated a degree of controversy as it has far-reaching implications in regards to international search results.
The Google ccTLD restriction has numerous practical SEO ramifications as user behavior was inherently and universally altered. As such, the traffic and clicks sites received internationally underwent an intrinsic shift, thereby impacting rank itself.
Google’s change in the algorithm that allowed it to restrict access to international SEO results and hyper-localize the SERP was picked up by the SERP Seismometer, which hit earthquake risk level of 64 on October 28th.
The update also impacted SERP features globally, with significant shifts in the frequency of AdWords ads, Local Packs, and Knowledge Panels on the SERP.
A Series of One-day Algorithm Roll-outs
Unconfirmed Update
Throughout the second half of September 2017, the SERP Seismometer caught a series of one-day fluctuation spikes that may constitute a Google algorithm update.
Starting on September the 13th, the seismometer caught four separate one day fluctuation spikes before the month was over. Meaning, that the last three weeks of September each contained at least one significant fluctuation increase, creating a pattern of sorts as each roll-out was a one-day event. In specific, other than the fluctuation caught on the 13th, the seismometer saw fluctuations on September 16th, 20th, and 28th with the fluctuation caught on the 20th being the most significant (as the seismometer reached an earthquake risk level of 77).
During each of these fluctuation events, industry chatter also indicated that Google had shifted the rankings. Indeed, the peculiar weekly pattern where one day spikes would occur within a few days of each other was also picked up by the industry. On September 27th, Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable reported on the beginning of the latest one day fluctuation event by starting off his article with, “Yea, yea, yea more of the same. Google is updating their search results…” The implication here being that the fluctuations being reported on existed in a larger context, one where Google has made multiple changes to the rankings within a short period of time that could possibly represent one drawn out update.
Elevated Fluctuations Impact Bottom of the SERP Sites
Confirmed Update
On June 23rd a prolonged series of increased rank fluctuations was initially tracked by the SERP Seismometer. The multi-day spike saw the seismometer hit earthquake risk levels as high as 85.
Though initial industry chatter was sparse, the industry began reporting on ranking shifts as the algorithm continued to update. By June 27th, Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable had seen enough chatter to describe the update as “legit” despite Google all but refusing to confirm the roll-out.
Upon executing a big data analysis, we determined that the most significant fluctuations were taking place for sites ranked between position 6 and 10 on the SERP. According to our research, while there were increased rank fluctuations occurring within positions 1-5, there was an evident and clearly observable uptick in the fluctuations upon reaching position 6 on the SERP. This data pattern held true across a multitude of niche industries that included Food and Drink, Travel, Retail and Consumer Goods, etc.
Google Update Hits Major Sites
Unconfirmed Update
On May 18th the SERP Seismometer tracked a one day Google rank fluctuation event. Reaching a moderate earthquake risk level of 71, the seismometer indicated that Google had released an algorithm update.
At the onset industry chatter was of a limited nature, as indicated by Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable. As time went on various theories as to what occurred were suggested. One such theory propagated that a test where some URLs corresponding to Featured Snippets were removed from organic results was responsible for the increased fluctuations.
However, our data indicates that this change, while only affecting 4.5% of all Featured Snippets, was not overly impactful and took on a consistent data trajectory that began on May 12th (six days before our seismometer tracked Google’s update).
Upon further investigation, our data indicated that Google had shifted the rankings of some of the most notable Ecommerce sites (i.e. Amazon, Best Buy, Overstock, eBay, etc.). Based on the data available to us, a large part of the rank fluctuations seen on May 18th were a result of Google altering its SERP placement of these notable sites.
Google Link Quality Update – Fred
Confirmed Update
On March 8th reports started filtering in that a Google algorithm update was brewing. First reported by SERoundtable, the initial speculation was that the developing update was related to link quality as black hat SEO forums had shown the most chatter.
As of the 8th our SERP Seismometer on desktop had not shown any abnormal rank fluctuations. However, our seismometer monitoring rank on mobile showed initial signs of an update, displaying moderate rank fluctuations. On March 9th the SERP Seismometer on desktop showed a significant spike in rank movement as indicated by an earthquake risk level of 79. Similarly, our mobile seismometer spiked to an earthquake risk level of 77.
Concurrent with the trends on the SERP Seismometer, industry chatter continued to rise. With chatter increasing, the notion of the update being related to link quality only solidified. As such, Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable reached out to Google for comment. Per usual policy, Google only offered vague comments about constant changes to rank. However, Googler Gary Illyes seemed to imply that indeed an update had occurred, indicating, jokingly, that all such ambiguous updates be called “Fred.”
As a result, the industry has adopted the name ‘Fred’ for the March 9 update.
After the initial rollout, and a three day respite from elevated rank fluctuations, the SERP Seismometer on desktop saw another fluctuation spike. Taking place over two days (March 13 -14), the seismometer recorded an earthquake risk level high of 100 on the 14th.
The second phase of ‘Fred’ brought with it what is perhaps clarification as to its nature. Though Google still did not comment on the algorithm, SearchEngineLand reported that the update targeted sites engaged in over-advertising. That is, sites that engage in excessive advertising to drive revenues while providing poor and inferior content.
Significant Algorithm Update Roll-out
Confirmed Update
From February 7th through the 10th the SERP Seismometer reported heightened levels of rank fluctuations on desktop. This series of increased fluctuations reached a substantial earthquake risk level high of 97 on February 9th.
Corresponding to the rank fluctuations on desktop, our mobile seismometer similarly showed an increase in mobile rank fluctuations on February 8th that lasted through the 10th. Like desktop, rank fluctuations reached a high on February 9th hitting an earthquake risk level of 90.
At the onset, Barry Schwartz reported this algorithm event on SERoundtable, indicating that there had been some, though not extensive chatter within the SEO community regarding changes in rank.
As the algorithm continued its roll-out, it became apparent that this was a major ranking event (as indicated by the significantly high fluctuations seen on February 9th as per the SERP Seismometer). With additional reports of rank changes coming in from the SEO community, SearchEngineLand reported that the update may have been related to the Panda algorithm.
Google has yet to comment on the matter.
Possible Update to Google’s Penguin Algorithm
Unconfirmed Update
According to our rank fluctuation seismometer, there was a Google algorithm event that took place between February 1st and 2nd. On both days, the SERP Seismometer for desktop showed heightened, though not excessive, earthquake risk levels that reached 69.
The SERP Seismometer monitoring mobile rank fluctuations presented an increase on both days as well. However, on February 2nd the seismometer for mobile showed a slightly more elevated earthquake risk level of 70.
SearchEngineLand reported on the algorithm event, indicating that an update may have been made to Google’s Penguin algorithm. This theory was supported by an increase in rank change chatter within the “black hat” SEO community, indicating that the update had to do with spammy link practices. This theory was neither confirmed nor denied by Google themselves.
Elevated Fluctuations Point Towards Minor Update
Unconfirmed Update
On January 24th, our SERP Seismometer, monitoring rank fluctuations on desktop, tracked a one day Google algorithm update event. The seismometer indicated that there were significant changes in rank within Google as an earthquake risk level of 77 was indicated.
Though a one day event on desktop, our mobile seismometer showed the algorithm event taking place over a three day period (from January 22nd through January 24). The algorithm event culminated with a January 24th earthquake risk level of 78, up from 67 on the 23rd, and 69 on the 22nd.
The Google algorithm update event produced increased rank change chatter within the SEO community. Barry Schwartz of SERoundtable indicated that he believed the update to be of a minor nature, though Google has yet to comment on the update.
Mobile Penalty
Confirmed Update
Per its August 2016 announcement Google has rolled out its intrusive interstitial penalty on mobile. Released on January 10th, the penalty demotes the rank of mobile sites employing overlays that cover all, or part of, page content.
Per Google’s initial August 23rd announcement, the following interstitial formats are considered intrusive:
Popups that cover, and as such prevent access to, essential page content.
Standalone overlays that require a user to dismiss them in order to view essential page content.
Layouts, wherein which the above-the-fold appears as if it is an interstitial, but where the page content per se is underneath the fold.
While the most common form of intrusive interstitial on mobile are ads, the penalty would penalize other forms of intrusive interstitials as well. To this extent Google has indicated that mobile country and language selectors that take the form of an interstitial are considered intrusive, and sites employing them could be penalized.
The penalty does not apply to all interstitial overlays. Those interstitials that are of a “responsible” nature, such as age verification interstitial overlays, do not fall under the scope of the penalty. Google has also indicated that should a site be hit by the penalty it will be restored upon reindexing, assuming the intrusive content has been removed.
2016 – Google Updates
SERP Seismometer Shows Mid-December Google Update
Unconfirmed Update
Starting on December 15th and hitting an earthquake risk level of 83 on the 16th, the SERP Seismometer picked up what the SEO community considered to be a Google algorithm update. Already on December 15th SearchEngineRoundTable noted that there appeared to be an algorithmic shift taking place. This assessment was corroborated by a heavy flow of chatter which indicated rankings were fluctuating on the Google SERP.
Similarweb’s SERP Seismometer that monitors mobile was even more volatile, showing a four day series of heightened fluctuation levels. This series of mobile rank fluctuations started on December 14th and ended on the 17th. During this four-day fluctuation event the seismometer hit an earthquake risk level high of 81 on December 16th.
To date, Google has not issued a comment, and as such has neither confirmed nor denied that they have rolled out an algorithm update.
Penguin 4.0
Confirmed Update
On September 23, 2016 Google announced that they updated the Penguin algorithm aimed at reducing spam in search results (Two examples of spammy practices targeted by this algorithm are keyword stuffing and linking schemes).
Previously, Penguin penalized an entire website that was found to employ “blackhat” SEO practices to advance their ranking.
Website owners penalized by Penguin have been desperately waiting for this update as the penalties remained in force until their websites were to be reevaluated at the next release of the algorithm. The last Penguin update occurred on October 17, 2014, almost two years ago.
Google stated that this update consisted of two major changes. The first is that Penguin has now been incorporated into Google’s core ranking algorithm which evaluates websites as it crawls them. As such, it will constantly be checking websites for their spam score. Websites that correct the issues that got them into trouble should see their rank improve the next time Google recrawls their pages.
The second change to the algorithm is that it no longer penalizes an entire website for spammy practices but analyzes the pages of a site on a more individual basis. This policy change can be seen in the language they chose in their announcement: Google now speaks of “devaluing spam” rather than penalizing websites.
“Penguin now devalues spam by adjusting ranking based on spam signals, rather than affecting ranking of the whole site.”
Google’s communique reiterated that their ranking algorithm includes over 200 signals but they did call out several specific ones saying “These signals include things like the specific words that appear on websites, the freshness of content, your region and PageRank.”
SERP Seismometer Points to Another Google Update
Unconfirmed Update
Following the spike of rank changes captured by our Google SERP Seismometer this week (see graph above),
there has been a lot of chatter about a Google update that seemingly took place sometime between Sept 9-12. It is not clear whether this was a continuation of the one that took place at the beginning of Sept (around Sept 2) or a separate one, but the rank volatility during both events is undeniable.
Elevated rank changes were recorded between Sept 8-11 with the seismometer spiking up to 83 on Sept. 10. The event that took place at the beginning of the month started on Sept 2 with the seismometer rising to 78 only to spike up drastically to 114 on Sept 3.
SearchEngineRoundTable documented a lot of the SEO industry chatter regarding these updates.
Google’s regular spokesmen, John Mueller and Gary Ilyes, have been mostly evasive when asked about the latest changes but John more or less affirmed there were changes that were rolled out. See his tweets:
Core Search Algorithm Update – Reported
Unconfirmed Update
On September 2nd, the SERP Seismometer began a two day fluctuation spike, with the seismometer hitting an unusually high earthquake risk level of 114 on September the 3rd. As early as September the 2nd, Barry Schwartz reported on Search Engine Land that industry “chatter” indicates that there was a core search algorithm update. Google has neither confirmed nor denied that there was indeed such an update.
Part of the “chatter” within the SEO community centered on local rankings, leading some to the conclusion that there were in fact two simultaneous algorithm updates, one to core search, the other to local rankings. Barry Schwartz reported this on his own site, seroundtable.com on September the 2nd. Google has yet to confirm or deny this update as well.
Our SERP Feature Tool tracked a dip in the number of Local Packs appearing on Page One of the SERP that occurred in conjunction with the update.
Possum Update
Confirmed Update
Rank Ranger’s SERP Seismometer, which measures fluctuations in the ranking of a data set 10,000+ domains and keywords, almost went off the scale on September 2nd, spiking up to 114. Several leading SEO analysts concluded decisively that a major algorithm update was rolled out by Google.
Barry Schwartz cited this volatility and chatter in industry forums as evidence of an algorithm update. Joy Hawkins, an expert in local SEO, said that based on her research and the results of her many clients who focus on local SEO, this update included a significant element aimed at reducing the number of duplicate and spammy listings in the local search results.
Possum, the name of the update coined by Phil Rozek and accepted by the local search community, alludes to the fact that many business owners think that they listings on Google My Business have disappeared, but they’re really just playing possum – they are still there, but they are being filtered out of the Local Pack and Local Finder. Read our blog “Google’s New Local Algorithm Update Known as Possum” for more information on the update.
The nature of the organic element of this update is not yet known, but we will provide more information as it becomes available.
Google has yet to officially confirm the roll out, but then of the thousands of updates they make each year, they confirm only a handful.
Mobile Interstitials Penalty
Unconfirmed Update
Google announced that starting January 1, 2017 mobile pages displaying intrusive interstitials may be penalized and their ranking negatively affected. Interstitials are various types of overlays covering all or part of the page the user wishes to view.
According to the official announcement on the Google’s Webmaster Central Blog, this update will target three types of interstitials which negatively affect the user experience:
Overlays that cover the content that the user wants to view – either immediately after landing on a page or after scrolling down
An interstitial that appears and blocks access to the desired content until the user dismisses it
Using a layout where the above-the-fold portion of the page appears similar to a standalone interstitial, but the original content has been inlined underneath the fold.
Google provided the following illustrations of interstitials that will negatively affect a page’s rank (note: the illustrations do not correspond to the three categories above that Google listed):
Google also listed three types of interstitials that would not result in a ranking penalty.
Interstitials that fulfill some legal requirement such as an announcement that the site uses cookies or that verifies the user’s age (where age limits apply to site usage)
A login form that gives the user access to content not available to anonymous visitors
Banners that cover up a relatively small portion of the screen. The example given are the banners offering to install mobile apps which normally appear at the top of the screen.
Mobile Friendly Update
Confirmed Update
In their quest to make the web more mobile friendly, Google’s John Mueller confirmed the completion of the rollout of the algorithm update (announced in March) that increases the effect of the ranking signal for pages that are relevant to a user’s search and are mobile-friendly.
Our Google Mobile SERP Features Tracker has been monitoring the Mobile-Friendly and AMP features (along with all SERP features) as they occur in mobile search. The Insight Graph below tracks the trends in Mobile-Friendly and AMP since May 1st when Google began rolling out their latest Mobile-Friendly update.
Undisclosed Activity
Confirmed Update
The SERP Seismometer level spiked at 93 during 7 days of continuous Google SERP Fluctuations from May 6th through May 13th.
Search Engine Roundtable’s Barry Schwartz reported that Google’s John Mueller indicated that to his knowledge the company had not rolled out a major algorithm update, but they do continue to make changes.
AdWords Update
Confirmed Update
Google announced on February 19th plans to remove classic sidebar ads in the side section of search engine results.
According to Matt McGee’s Search Engine Land article, there would be only two exceptions to this rule: Product Listing Ad (PLA) boxes and ads in the Knowledge Panel.
Barry Schwartz predicted in Search Engine Roundtable that the move away from sidebar ads will lead to four ads at the top of search engine results, the news of which triggered a frenzy of comments regarding the impact of such a change on small businesses and Google’s income.
Our Google SERP Features Tool reported this paid search update was rolled out on February 23, 2016. This search intelligence tool monitors trends in organic indicators, knowledge graph features, page one extras and organic results count on a 500k dataset and on February 23rd, in addition to zero sidebar ads, it reported an increase in bottom of the SERP ads of 26.79% in Google USA and similar results in other countries.
Core Quality Rank
Confirmed Update
Volatile fluctuations in both Desktop and Mobile search caused by a Google Core Quality Rank Algorithm update were reported by our SERP Seismometer, a SERP fluctuation monitoring tool used by SEO experts.
Google remained quiet as webmasters and SEO experts and bloggers buzzed with speculations. Search marketing expert Barry Schwartz asked Google’s John Mueller for confirmation of an algorithm update during the January 12th Webmaster Central Office Hours livestream, and published in Search Engine Land a statement indicating that “Google Panda is now part of Google’s Core Ranking Algorithm”.
The Panda algorithm is applied to sites as one of Google’s core ranking signals. It measures the quality of a site, based on Google’s guidelines and adjusts rankings.
2015 – Google Updates
HTTPS Update
Confirmed Update
Google announced that they’re now indexing HTTPS pages by default as user security is top priority. Sites using HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) are being rewarded with improved Google rank.
In situations where two URLs from the same domain seem to be sharing content, Google has a set of criteria it follows to determine whether it will serve the HTTPS or the HTTP page.
RankBrain Related Search Update (undisclosed)
Confirmed Update
Rank Ranger’s Features Graph analyzes SERP page 1 features data and stability for thousands of keywords per day, and on December 10th its reporting that Google’s RankBrain caused a boost in Google’s special SERP Features that resulted in a significant increase in the number of SERPs containing Related Search, as well as a quality improvement in the average word count of Related Search phrases.
Barry Schwartz mentioned in Search Engine Roundtable articles a December 10th shift and a potential Google Search Update on December 16th.
Google has not confirmed a major algorithm update, however, our analysis demonstrates RankBrain is causing search result changes.
Hacked Sites Algorithm
Confirmed Update
Google’s Hacked Sites Algorithm is expected to aggressively remove hacked sites from search results to improve the quality of search. The Webmaster Central Blog reported that “a huge amount of legitimate sites are hacked by spammers and used to engage in abusive behavior, such as malware download, promotion of traffic to low quality sites, porn, and marketing of counterfeit goods or illegal pharmaceutical drugs, etc.”
It is expected that this update will impact roughly 5% of queries across the board in multiple languages.
Our SERP Seismometer reported red zone Google SERP fluctuations on Desktop on October 8th and has continued on Mobile search for several days.
Search Engine Roundtable’s Barry Schwartz obtained confirmation from Google’s Gary Illyes that this algorithm only impacts spammy queries.
Panda 4.2
Confirmed Update
Panda 4.2 is the first refresh of Google’s Panda quality content policing of the web since September 2014. Bad news for spammy link farms and sites with low quality content, this refresh should be welcomed by sites that were penalized by Panda 4.1 – if they have corrected the issues that caused them to be penalized by Google. As with previous Panda updates, sites may notice an increase in organic ranking, be mildly affected of suffer a rank penalty depending upon the quality of their content because Google’s goal is to provide the best search experience for users of Google’s various search engine services.
Our SERP Seismometer reported red zone Google SERP fluctuations on both Desktop and Mobile search on July 18th.
Google has reported to Search Engine Land’s Barry Schwartz that Panda 4.2 has impacted 2% to 3% of English language queries.
Google Core Quality Update
Confirmed Update
Spikes in Google Desktop SERP fluctuation from the end of April through mid-May were finally verified by Google as a core algorithm change relating to quality signals that they use in determining rank.
For weeks Google did not release a statement, while SEO forums buzzed with complaints and questions. NBC News reported on a Google ‘phantom’ algorithm update on May 13th after HubPages reported a 22% drop in search traffic.
Search Engine Land’s Barry Schwartz received confirmation from a source at Google on May 19th that “there were changes to its core ranking algorithm in terms of how it processes quality signals. It was an update to the overall ranking algorithm itself”.
Google Mobile-Friendly
Confirmed Update
Mobilegeddon hype swept the web for weeks leading up to Google’s mobile-friendly ranking factor algorithm update. Adding mobile-friendliness as a ranking signal affects mobile searches internationally, across all languages. This can have a significant impact on search results, while providing better and more relevant data for users.
Business Insider’s Jillian D’onfro predicted that the mobile-friendly algorithm update “could crush millions of small businesses”.
While Computer World’s senior report Sharon Gaudin published a helpful guide: “How to prep, in 7 steps, for Google’s mobile search change”.
Here in the Bat Cave (aka Rank Ranger Development HQ), a new tool was developed to help you monitor Google Mobile SERP Fluctuations.
Google announced that this update would roll out gradually beginning on April 21st, however, our Mobile Search SERP Seismometer caught significant mobile search fluctuations beginning on April 18th, which may have been caused by testing or the beginning of this gradual roll-out that is expected to occur over several weeks.
Undisclosed Activity
Confirmed Update
The SERP Seismometer showed a major spike in algorithm volatility, leading to the belief that there was a major Google update, however nothing has been confirmed yet.
Search Engine Land reported that Google has said this is not related to Penguin or Panda.
2014 – Google Updates
Google Local Algorithm Expands
Confirmed Update
The Local Algorithm was originally launched in July 2014, and has now been expanded to English speaking countries globally. This update is known by the industry-given name of Pigeon and allows Google to provide more accurate and relevant information regarding local searches.
The Local Search Forum was one of the first sites to report major shifts in rankings of local results and later confirmed that this was a Google update.
Rank Ranger’s Shiri Berzack discusses Google Pigeon’s Flight Plan.
Mike Blumenthal, from blumenthals.com, discusses what to expect from the Local Update for those in the UK, Canada, Australia, New Zealand and other English speaking countries.
Penguin 3.0 Extended
Confirmed Update
The Penguin Algorithm has had significant change since its first appearance in April 2012, and now a Google spokesperson has confirmed that the major, infrequent updates will be replaced by a steady stream of minor updates.
The spokesperson told Search Engine Land:
“That last big update is still rolling out [referring to Penguin 3.0]— though really there won’t be a particularly distinct end-point to the activity, since Penguin is shifting to more continuous updates. The idea is to keep optimizing as we go now.”
Our own Shiri Berzack discusses this move towards a steady stream of Penguin updates and the positive effects it could have on businesses moving forward.
On the other side, Jill Kocher, from Practical Ecommerce, discusses the challenges this could place on companies particularly when trying to decipher reasoning behind declines or increases in traffic.
Pirate Update #2
Confirmed Update
Pirate Update #2 should not affect a wide variety of sites since it specifically targets only those that have received DMCA takedown requests. In August of 2012 Google pushed out their first Pirate update by filtering down (or completely out in documented cases) pirated content in their attempt to help copyright owners.
Google’s Public Policy Blog explains how they are combating piracy across all Google services.
Torrent Freak published an article discussing the update and its effect on various websites.
Rank Ranger’s Shiri Berzack shares her thoughts in Google Pirate Update Fights Piracy
Penguin 3.0 Update
Confirmed Update
Pierre Far, Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google UK, has confirmed their roll-out of the Penguin 3.0 algorithm update on Friday, so far affecting fewer than 1% of queries in the US English search results.
This is great news for anyone hit in October 2013 with a Google penalty during the Penguin 2.1 update, as Google’s John Mueller confirmed recently in the Google Webmaster Central Help Forum that if you’ve corrected the situation that caused the penalty “you’d need to wait for the algorithm and/or its data to refresh to see any changes based on the new situation”. Further elaborating on that, Pierre Far posted:
“This refresh helps sites that have already cleaned up the webspam signals discovered in the previous Penguin iteration, and demotes sites with newly-discovered spam.
It’s a slow worldwide rollout, so you may notice it settling down over the next few weeks.”
Stephen Kenwright of Branded3 in his Google Penguin 3.0 Damage Report provides an assessment of how Penguin 3.0 is affecting the more than 125,000 keywords they run daily rank tracking on and discusses how to recover from a Penguin update.
Panda 4.1
Confirmed Update
Panda 4.1 is a significant update to the Panda algorithm that targets low quality content with greater precision. This update is expected to identify low-quality content and result in greater diversity of higher rankings for small and medium-sized sites containing good quality content. It is a gradual global roll-out expected to affect approximately 3-5% of queries.
Google’s official announcement was made by Pierre Far on Google Plus.
Providing interesting insight, Bill Slawski of SEO by the Sea walks readers through the logic of a recent Google patent application that may be behind this latest Panda update.
The Webmaster World forum chat has been a mix of positive and negative with most medium size businesses doing well, but some smaller businesses suffering drops in SERPs.
Google Authorship Removed
Confirmed Update
For months Google has been analyzing Authorship from a user’s perspective and effectiveness for potential clicks. With this update Authors lost their edge as Google decided to stop showing authorship in search results.
Official Announcement from Google’s John Mueller
Our very own Barry Schechter’s Google Authorship is No More post
Danny Sullivan reports that Google Authorship My Be Dead, But Author Rank Is Not
HTTPS Update
Confirmed Update
HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) is the new ranking signal. According to Google, secure sites may be given a ranking boost for the added security.
Google Webmaster Central Official Announcement
Google’s Support documentation on Securing your site with HTTPS
Google Local Algorithm Update
Confirmed Update
Google launched an update to their local search algorithm to help them provide more accurate and relevant local search results.
The chat in the Webmaster World Local Search Forum suggests that the update was causing inconsistent results, with “major flux” still occurring a week after the rollout.
Payday Loan Algorithm 3.0
Confirmed Update
Google rolled out an update to their PayDay Loan Spam Algorithm. Version 3.0 targets the queries for ‘payday loans’, ‘casinos’, ‘accident claims’ and a variety of others that return an excessive number of web spam results.
Google’s Matt Cutts announced this algorithm update on Twitter.
Matt Southern reported in Search Engine Journal that “unless you’re running a site in a niche that Google would consider to be ‘very spammy’, there is very little for you to be personally worried about with this update.”
Panda 4.0
Confirmed Update
Our SERP Seismometer has been showing sharp fluctuations in recent weeks causing lots of chatter in SEO and webmaster forums. By mid-May we started to see a relative calm, but suddenly the red alert went up again and shortly after that Matt Cutts announced on Twitter that Google had launched Panda 4.0 and plans to be rolling out more updates.
The goal of Panda has been to penalize poor content quality and scraper sites, while boosting sites with great content up in the SERPs and thereby providing Google users with high quality results.
Google’s Matt Cutts announced Panda 4.0 on Twitter.
Tim Worstall shares in Forbes his take on this Evolution In Action; Google’s New Panda 4.0 Rollout
Payday Loan Algorithm 2.0
Confirmed Update
Google announced the release of an update to their Spam Algorithm that targets the type of queries that return an excessive number of spammy results. This specific update was an international rollout that is reported to affect different languages to different degrees and noticeably impacts English queries by about 0.2%.
Matt Cutts Tweeted: “This past weekend we started rolling out a ranking update for very spammy queries.”
Search Engine Watch reported “Over the weekend we began rolling out a new algorithmic update,” a Google spokesperson told SEW. “The update was neither Panda nor Penguin – it was the next generation of an algorithm that originally rolled out last summer for very spammy queries.”
Algorithm Activity – Undisclosed
Confirmed Update
The SERP Seismometer has been indicating volatile activity by Google for much of April. Lots of chatter in the various webmaster and SEO forums and blogs about dramatic SERP changes, but no official announcement from Google.
Undisclosed Activity
Confirmed Update
Webmaster and SEO forum rumors of a Soft Panda update around March 24th match up with the red zone dates displaying in our SERP Seismometer, however, no official announcement has been made by Google.
Top Heavy 3 Update
Confirmed Update
Google’s Page Layout Algorithm targets pages with disproportionate number of ads above the fold in relation to page content.
Google’s Matt Cutts confirmed this algorithm refresh in a Tweet.
Page Layout Algorithm’s goal is to make users’ search experience more efficient and quick, enabling them to reach the content they’re seeking.
2013 – Google Updates
Authorship Rich Snippet Update
Confirmed Update
In what may be the most dramatic Google update of 2013, Authorship & Rich Snippet results dropped as much as 15% as Google tightened the qualifications for rich snippets. Authors reported problems and were advised to refer to Google’s rel=”author” FAQs to ensure they’re following the rules.
Chatter at the Webmaster World forum indicates significant negative SERP changes.
Undisclosed Activity
Confirmed Update
Our SERP Seismometer indicates an update in the algorithm. Lots of chatter in the various webmaster and SEO forums and blogs about SERP changes, but no official announcement from Google.
Penguin Update 5 (ref 2.1)
Confirmed Update
Penguin 2.1 (Penguin 5th edition) was released in Google’s continuing battle against web spam. We see a corresponding spike in the SERP Seismometer on October 5th.
Search Engine Journal reports: Penguin 2.1: What Changed Since 2.0, and How to Recover
Hummingbird Update
Confirmed Update
Hummingbird, released around August 21st, is a new search algorithm that Google developed with a focus on Semantic Search. Their goal is to provide more personalized results based on your online behavior, location, trends, etc. The SERP Seismometer (RRI) captured this significant change on August 21st.
Search Engine Land provides this useful FAQ: All About The New Google “Hummingbird” Algorithm
Undisclosed Activity
Confirmed Update
JULY 26, 2013
The SERP Seismometer spiked so we know that something is brewing over at Google, but they have yet to confirm exactly what it is.
A forum discussion at Webmaster World indicates signs of a soft Panda update.
Panda Update 26
Confirmed Update
As Google was either testing or rolling out the new multi-week algorithm update that Matt Cutts mentioned on Twitter, the SERP Seismometer soared into the danger zone. This update targets websites with low-quality content. Although some sources report that Google released an update on June 18th, our SERP seismometer indicates that the affects of this update were strongest on the 28th.
This is a good time to revisit Search Engine Land’s SEO Guide which outlines and provides possible responses to Violations & Search Engine Spam Penalties
Payday Loan & Google Dance
Confirmed Update
The latest in Google’s Panda update can cause a site’s rankings to dance up and down for days based on the Panda’s perception of site content quality. It also addresses the Payday aspect, which is an international update targeting spam in the form of payday loans and porn.
Google’s Matt Cutts addresses what a site owner should do if they think they have been negatively affected by Panda.
Search Engine Land reports on Google Payday Loan Algorithm: Google Search Algorithm Update To Target Spammy Queries.
Penguin Update 4 (ref 2.0)
Confirmed Update
Newer generation Penguin enables Google to dig deeper into sites for web spam according to Google’s Matt Cutts a few hours before this release. The update will have a greater impact on SEO and webmasters.
Read more in Search Engine Land’s announcement of Penguin 2.0.
Phantom
Confirmed Update
Lots of volatile activity as Google’s Phantom wreaked havoc on many sites according to the buzz in SEO and webmaster forums. The SERP Seismometer validates this update as it shows that from May 7 – 14 Phantom was creating higher flux than usual.
Panda Update 25
Confirmed Update
Panda update #25 is another attempt by Google at dealing with spammers and people who abuse the system.
Search Engine Journal reports on: Matt Cutts announcement at SMX. Cutts recommends using Fetch as Googlebot tool to view sites the way Google sees them.
Panda Update 24
Confirmed Update
Google announced this as a Panda refresh with an approximate impact of 1.2% of English search results.
Search Engine Journal offers Important SEO Habits to Adopt for Post Panda-Penguin Era Survival
2012 – Google Updates
Panda Update 23
Confirmed Update
Panda update affects about 1.3% of English search queries and comes as a surprise during the last minute holiday shopping season.
Search Engine Land provides some advice on how to stop the panic.
Panda Update 22
Confirmed Update
This 22nd refresh of Panda was reported to affect 0.8% of English queries.
Search Engine Journal offers an overview of the update along with tips on Overcoming the Google Panda, EMD and Disavow Updates.
Panda Update 21
Confirmed Update
Panda Update 21 was reported to affect 1.1% of English queries.
Search Engine Land discusses the update in more detail.
Top Heavy 2 Update
Confirmed Update
Google’s Page Layout Algorithm targets pages with disproportionate number of ads above the fold in relation to page content. This update affected approximately 0.7% of English queries.
Read more at Search Engine Land about this update.
Penguin Update 3 (ref 1.3)
Confirmed Update
This multilingual Penguin refresh has been reported as small, but far reaching in an international sense.
Search Engine Land covers Matt Cutts’ announcement while Search Engine Journal discusses strategies for a post Panda, Penguin world.
September Roundup – 65 Updates
Confirmed Update
Targets content quality in addition to a batch of Google feature changes.
Highlights of the 65 changes have been published in The Official Google Search Blog.
Panda Update 20 and Exact Match Domain
Confirmed Update
Two big updates, Panda 20 and EMD (Exact Match Domains). This EMD update changes the way Google handles Exact Match Domains by reducing low quality matches. The Panda update was a fairly big one affecting the queries of approximately 2.4% of search results.
Webmaster World members discuss the affects of these updates.
Search Engine Land covers the crackdown on low quality exact match domains.
Panda Update 19 (ref 3.9.2)
Confirmed Update
Reported as a minor data refresh affecting less than 0.7% of queries.
Search Engine Land talks about this update.
Panda Update 18 (ref 3.9.1)
Confirmed Update
Google reported this Panda update as a data-refresh and it affected less than 1% of queries.
Read more about this refresh at Search Engine Land.
7 SERPs Is The New 10
Confirmed Update
It looks like Google may be moving away from their traditional 10 listings per page to only 7 results per page, and with a new format of expanded detail for the site in the number 1 position.
Search Engine Land reports: 7 Is the New 10? Google Showing Fewer Results & More From Same Domain
Pirate Update #1 / DMCA Penalty
Confirmed Update
With the Pirate Update, Google aims to help copyright owners by filtering down or out (with documented proof) pirated content. For example, websites with multiple submitted copyright removal notices will be ranked much lower in Google results. It will also be possible that links will be dropped from Google completely in cases of valid copyright removal notice submission.
The official Google Blog writes about the update to their search algorithms.
Danny Sullivan of Search Engine Land reported that this Pirate Update is Google’s response to a challenge from Hollywood movie mogul Ari Emanuel, co-CEO of William Morris Endeavor, who compared stealing copyrighted material to child pornography, suggesting that Google’s team should be smart enough to be able to filter out pirated content in the same manner.
Panda Update 17 (ref 3.9)
Confirmed Update
Panda 3.9 didn’t make too large of an impact on results, although many sites saw fluctuations for 5 or so days after the update.
Search Engine Journal’s The Holy Grail of Panda Recovery – A 1-Year Case Study is an entertaining and informative read.
Search Engine Land talks about Google pushing out Panda 3.9.
Link Checks
Confirmed Update
Webmasters received pre-penalty warnings as Google continued their push for compliance of Google Webmaster Guidelines regarding unnatural or artificial backlinks. Then Google backtracked with a “never mind”, followed shortly by instructions that it is a website’s responsibility to get the bad links removed, and the cycle repeated. Bottom line: track down the bad links, request removal and report violations to Google.
Search Engine Land provides an entertaining and informative chronology in their Insanity: Google Sends New Link Warnings, Then Says You Can Ignore Them article.
Panda Update 16 (ref 3.8)
Confirmed Update
A smaller impact change with data-only updates, no changes to the algorithm.
Shout Me Loud discusses What To Do Next with Google 3.8.
Read about the Official Google Panda Update 3.8 at Search Engine Land.
Panda Update 15 (ref 3.7)
Confirmed Update
Panda 3.7 rolled out with less than 1% affect on US & Worldwide search results.
Search Engine Land talks about the update.
May Roundup – 39 Updates
Confirmed Update
May saw 39 updates. The highlights of these include detecting inorganic backlinks, editing page titles and improving freshness.
Read Google’s list of all the updates on their official blog.
Search Engine Land gives an overview of the May updates.
Penguin Update 2 (ref 1.2)
Confirmed Update
Penguin’s first update was labeled a “data refresh” by Google with assurances that it would affect less than 0.1% of English searches.
Search Engine Land reports on what they’re labeling as Penguin 2 and provides an overview of how one site recovered from this update.
April Roundup – 52 Updates
Confirmed Update
These 52 minor updates were mostly tied to the Penguin update from earlier in 2012. Updates included indexing, spelling, site links, sports scores features and more.
Google outlines the 52 updates in their official blog.
Search Engine Land provides some insights in Penguin or Panda? How To Determine Which Google Algorithm Update Impacted Your Website.
Panda Update 14 (ref 3.6)
Confirmed Update
Another Panda refresh with few implications.
Search Engine Land reports on the official Panda 3.6 update.
Penguin Update 1 (ref 1.0)
Confirmed Update
Intended to penalize black hat webspam techniques that don’t benefit site visitors, such as keyword stuffing and link schemes that attempt to manipulate SERPs, Penguin Update 1 rewards those in compliance with Google’s publishers guidelines.
The Google Blog looks into rewarding high-quality sites with this update.
Search Engine Land reports: Google Launches “Penguin Update” Targeting Webspam In Search Results and offers some Recovery Tips & Advice.
Panda Update 13 (ref 3.5)
Confirmed Update
A quiet update of Panda that helped big brands and news sites, but wasn’t necessarily bad for anyone else.
Look at the Winners & Losers from this update with Search Engine Land.
The Google Webmaster Blog called it: Another Step to Reward High Quality Sites.
March Roundup – 50 Algorithm Updates
Confirmed Update
A range of 50 updates to the algorithm.
The official Google blog talks more about these 50 updates.
Search Engine Land goes into the updates, specifically anchor text, image search, navigational search and more.
Panda Update 12 (ref 3.4)
Confirmed Update
An update affecting 1.6% of searches and targeting low quality websites.
Search Engine Land talks about Panda update 3.4 rolling out.
TechWise goes into the updates and gives more clarification.
Venice, Panda Update 11 (ref 3.3) & 38 more
Confirmed Update
According to Google, in February they rolled out a combination of updates: Venice which “improves the triggering of Local Universal results by relying more on the ranking of our main search results as a signal”, a Panda refresh “making it more accurate and more sensitive to recent changes on the web” and 38 smaller search quality improvements.
The Official Google Search Blog details Search quality highlights: 40 changes for February.
Search Engine Land reports on Why Google’s Venice Update Fundamentally Changes Global SEO.
A summary of the Panda and search quality updates is provided by Search Engine Land.
Top Heavy 1 Update
Confirmed Update
This update penalized sites that were too “top-heavy”, meaning that they had too many ads above the fold on their page.
The Google Webmaster Central Blog spoke about this update.
Search Engine Land tells us: The Top Heavy Update: Pages With Too Many Ads Above The Fold Now Penalized By Google’s “Page Layout” Algorithm
Panda Update 10 (ref 3.2)
Confirmed Update
A data refresh that didn’t actually involve a Panda algorithm change, but rather updated Google’s data on the sites that were affected by Panda.
Search Engine Land reports on the update.
Are You Making These 7 Panda-Punishing Content Mistakes? Find out at Search Engine Journal.
January Roundup – 30 Search Quality Updates
Confirmed Update
This series of updates targeted improvements to the algorithm that include local and image search relevancy, SafeSearch, encryption, country restricted search and more.
The Official Google Search Blog provides the full list including codenames.
2011 – Google Updates
December Roundup – 10 Updates
Confirmed Update
A second round of 10 updates including results refinement, comprehensive indexing, better auto-complete, “parked-domains” classifier and more.
The Official Google Search Blog details these search quality algorithm changes.
Panda Update 9 (ref 3.1)
Confirmed Update
Panda’s 9th update was a minor update affecting less than 1% of all searches.
Talking about the minor update with Search Engine Land.
November Roundup – 10 Updates
Confirmed Update
Google announces 10 small recent updates including rich snippets, cross-language support, refreshes and other factors that affect how search results are ranked and displayed.
Google shares the methodology and process behind their search ranking, evaluation and algorithmic changes and details these 10 updates in their Official Google Search blog.
Freshness Update
Confirmed Update
Promoting fresh posts, this update puts a focus on fresh content and regular updates, affecting 35% off all searches.
Google’s official blog details how they’re giving you fresher content.
Search Engine Land talks about the impact of freshness.
Panda Update 8: Flux
Confirmed Update
With all the roll-outs, there was bound to be some flux in the Panda updates. Google’s Matt Cutts tweeted “Weather report: expect some Panda-related flux in the next few weeks, but will have less impact than previous updates (~2%).”
Search Engine Land looks into the flux.
Search Engine Watch tells us what to expect and what to look for.
Panda Update 7 (ref 2.5)
Confirmed Update
This update focuses on a wider reaching analysis of site content quality.
WebProNews reports DaniWeb Loses Over Half of Traffic: The Panda is Back and Dani discusses recovering credibility with Google.
Panda Update 6 (ref 2.4)
Confirmed Update
Expands Panda reach from changes in search for English to algorithmic search improvements in all languages except Chinese, Japanese and Korean (which Google is currently testing).
Google Webmaster Central Blog announces High-quality sites algorithm launched in additional languages.
Webmaster World members discuss “Google Panda 2.4 – Now in All Languages!”
Panda Update 5 (ref 2.3)
Confirmed Update
Update 5 expands Panda’s ability to distinguish between higher and lower content quality, resulting in higher quality content for the end user.
Search Engine Land looks into the update.
Panda Update 4 (ref 2.2)
Confirmed Update
This update targets sites that scrape content from its original source, to prevent the violators from ranking higher than the original content owner.
Search Engine Land gives us some insight into Panda update 2.2.
Webmaster World members ask “Why haven’t sites come back from Panda?” and Matt Cutts explains Google’s perspective during an interview with Danny Sullivan at SMX.
Panda Update 3 (ref 2.1)
Confirmed Update
A minor update to Panda with no official announcement from Google.
Search Engine Journal discusses the obsession with Panda updates.
Panda Update 2 (ref 2.0)
Confirmed Update
Panda expands target beyond US borders targeting all English language search results and incorporates user feedback signals.
Google details the change in their Webmaster Central Blog: “High-Quality Sites Algorithm Goes Global, Incorporates User Feedback”
Search Engine Journal outlines what Panda did and why.
Plus 1 Button
Confirmed Update
Google introduces the +1 button allowing optimization through recommendation.
The Official Google Webmaster Central Blog announced the +1 button with a full explanation of the uses and effects.
Panda Update 1
Confirmed Update
Google launched their Panda update, changing their algorithm by targeting link farms and low quality content. This major update affected 12% of searches and was the beginning of a new era in SEO.
Web Master World opened a discussion on this update which is related to what Matt Cutts spoke about in his blog. Google published two blog posts to help with this update: Another step to reward high quality sites and
More guidance on building high quality sites.
Wired.com provides some detail about this launch “The Panda that hates farms“.
Wikipedia and Search Engine Land explain more about Panda and the update.
2010 – Google Updates
Google Instant
Confirmed Update
Google Instant launched making the entry of search faster by automatically suggesting options for completion of a search term. Google reports that 15 different technologies were utilized to make this functionality possible.
Read more about Google Instant.
The Official Google blog talks about their unveiling of Google Instant.
Caffeine Update
Confirmed Update
Caffeine is Google’s new web indexing system that is expected to provide 50% fresher content in searches than their previous index and create the largest collection of web content Google has ever offered.
Google’s Official Blog introduces the Caffeine.
Mayday Update
Confirmed Update
Mayday included a number of updates toward the end of April that looks for higher quality sites to surface for long tail queries.
Search Engine Land explains the Mayday updates.
Webmaster World members scream “Mayday!” and discuss how this update hit them.
Google Places
Confirmed Update
The introduction of Google Places created a better way for people to search and find local businesses. This update turned Google Local Business Center to Places.
Google’s Official Blog talks about Places and the impact for businesses.
2009 – Google Updates
Caffeine Introduction
Confirmed Update
Google gives a sneak preview of their next-generation infrastructure and invites people to help test it. To help them with improvements they instruct to include the word “caffeine” in the feedback form.
The Google Webmaster Central Blog unveils their secret project.
Search Engine Land provides their perspective on how this new search index might affect web developers and SEOs.
Vince Changes
Confirmed Update
Vince changes focus on trust, authority and reputation to provide higher quality results which could push big brands further to the top of the SERPs.
Google’s Matt Cutts responds to the question “Is Google putting more weight on brands in rankings?” Matt also tells us that Vince is the guy who worked on the changes and that this is not an update.
There’s some buzz over at Webmaster World as members respond to search results fluctuation.
2008 – Google Updates
Google Suggest
Confirmed Update
In a major update, Google introduces the Suggest feature. As you begin to enter your search query, Google now attempts to auto-complete your query by suggesting related search terms.
Search Engine Land displays how Google Suggest works.
Refer to Google’s Help on Autocomplete for more info.
Dewey Update
Confirmed Update
The Dewey update caused a stir in the SEO community but the specifics were unclear. There were some big changes in Google search results, but no more than that.
Read more about it at Search Engine Land.
2007 – Google Updates
Buffy Update
Confirmed Update
Buffy seems to be a collection of a number of small updates with an impact on single word search results, as well as various other factors.
This update was discussed and named by members of Webmaster World.
Universal Search
Confirmed Update
Universal Search, as the name implies, makes searches universal by combining results from Google’s web, blog, news, video, images, local and book searches.
Google’s Official Blog announces the feature and provides examples.
Search Engine Land calls Universal Search the most radical change to Google’s search results ever.
2005 – Google Updates
Big Daddy Update
Confirmed Update
An infrastructure update changing the way Google dealt with URL canonicalization, redirects and more. This update was started on November 2005 but not fully deployed until the end of March 2006.
Webmaster World members discuss their suspicions regarding an update weeks in advance of any official news.
Search Engine Promotion reports “In contrast to the usual algorithm updates, this update will be much bigger because it changes the way Google works behind the scenes.”
Update May 2006: Matt Cutts provides a chronology of Big Daddy.
Jagger Update
Confirmed Update
A significant update, Jagger targeted low quality links as well as link farms, in order to reduce spamming.
Search Engine Journal reports Google Jagger Update is Official.
Google Local and Maps Merge
Confirmed Update
Searchers can now find both local search and mapping information together on the same search results page using Google Maps.
Google News announces Google Merges Local and Maps Products
Gilligan Update
Confirmed Update
Google said that Gilligan was not an update but rather a refresh, however this was a major change to the search engine’s underlying index. It was later referred to by some as “False Alarm”.
Search Engine Watch talks more about Gilligan and False Alarm.
Matt Cutts says it was not an update.
Personalized Search
Confirmed Update
Search gets personal according to Google. By using your personal search history, Google makes results more personal and more accurate for you.
The Google Official Blog explains personalized search.
Google Sitemaps
Confirmed Update
The Google Sitemaps program allows webmasters and site owners to create XML files containing URLs they want Google to crawl (along with freshness data) and submit via Google Webmaster Tools for possible inclusion in Google’s web index.
Search Engine Watch provides details and clarification from Google’s Shiva Shivakumar, engineering director and technical lead for Google Sitemaps.
Bourbon Update
Confirmed Update
Bourbon update affected 3.5% of queries, the update changed the algorithm in terms of how duplicate content and non-canonical URLs are handled.
More on this update in a discussion at Webmaster World.
Allegra Update
Confirmed Update
Allegra is Google’s LSI algorithm, which affected some scoring factors and other smaller tweaks.
See the discussion at WebMaster World.
NoFollow Attribute
Confirmed Update
A small yet important feature, the NoFollow attribute combats comment spam. Webmasters can use the attribute to automatically add rel=”nofollow” to links that site visitors add in comment areas and Google will do their part by not giving any inbound link credit to the sites those links are directed at. Not only was Google involved in this but Microsoft (MSN Search) and Yahoo came on board.
Google’s Official Blog. provides an informative Q&A.
Wikipedia provides additional information.
2004 – Google Updates
Brandy Update
Confirmed Update
The Brandy update caused changes that include an expansion of Google’s index, along with a focus on anchor text relevance, inbound link quality defining your online neighborhood, and Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI).
Chatter about this update began at Webmaster World on February 13th.
Austin Update
Confirmed Update
In the aftermath of the November Florida update, Austin has swept in to attack unconventional practices even further. Although this update was intended to be an improvement, many sites were hit hard by this change in the algorithm according to the buzz in various webmaster forums.
Search Engine Journal delves into what Austin is all about.
2003 – Google Updates
Florida Update
Confirmed Update
Florida is a large and aggressive update that has rattled the SEO world. Many big sites have lost ranking and the community outcry is unprecedented.
Search Engine Watch delves into the Florida update and provides helpful Q&A.
The Web Workshop sums up some theories about what happened and answers the question “Where do we go from here?”
Fritz Update
Confirmed Update
Google switched from monthly index updates to a process that updates a percentage of the index every day for faster, more accurate information. The smaller day-to-day changes are being referred to as everflux.
Webmaster World members discuss the Fritz update.
Update December 2006: Matt Cutts explains the difference between Google Dance, the everflux caused by Fritz, and the new streamlined process that he says regular people won’t notice – and that the rest of us will refer to as algorithm updates and data refreshes.
Esmerelda Update
Confirmed Update
Esmeralda continues where Cassandra and Dominic left off in Google’s battle against the manipulative practices of hidden text/links and poor quality backlinks.
Ranking and backlink issues are discussed by members of Webmaster World.
Dominic Update
Confirmed Update
Google again updated the way they crawl the internet, fine tuning their skills and battling manipulative link practices.
The volume of discussion surrounding Dominic caused the folks at Webmaster World to break the discussion into multiple parts in an effort to dissect the issues.
Cassandra Update
Confirmed Update
Cassandra’s focus seems to be on link-quality issues, hidden text and hidden links. This was also the first time Google has allowed banned sites to submit a reconsideration request.
Webmaster World members discuss changes in keyword weight, banned sites, site age, redirects, rank position and more.
Boston Update
Confirmed Update
This was the first named update in which Google improved their algorithm to further analyze backlink data which made a major impact on SERPs.
Webmaster World members express excitement over the Boston update.
2002 – Google Updates
Google Dance Began
Confirmed Update
Google’s first major update, Google Dance appears to include a significant change in relevance ranking and an increased importance of anchor text quality.
This algorithm update has stirred up more than 500 messages in a discussion at the WebMaster World forum.
2000 – Google Updates
Google Toolbar
Confirmed Update
The Google Toolbar launched. This browser plugin allows users to perform a Google search from any web page and search within any website even if that site doesn’t have it’s own search engine.
Google’s Official Announcement outlines the features and benefits of this free tool.
20001 – Google Updates
April 21st Unconfirmed Update
Unconfirmed Update
On April 21st, the SERP Seismometer tracked a massive spike in rankings on both mobile and desktop. It’s interesting to note that there were high-level fluctuations leading up to the spike starting on April 18th. The fluctuations returned to normal on April 23rd.
On April 21st, Barry Schwartz of Search Engine Roundtable reported high levels of industry chatter.
Track Gen-AI And Organic KPI's On The #1 SEO Platform
Give it a try or talk to our marketing team - it’s free!