Everything You Need to Know About 301 Redirects

Are you planning a website update? Then don’t let broken links cost you traffic or customers.
Changing a site is often unavoidable—whether to improve mobile compatibility, refresh your branding, or implement a new design. However, they can sometimes cause visitors to encounter broken links, resulting in lost traffic and missed business opportunities.
The way to avoid this is with a 301 redirect. It allows website owners and SEO specialists to ensure every user reaches the right pages while maintaining SEO rankings.
By the end of this post, you will know:
- What 301 redirects are
- Why they are important
- Best practices on how to implement them
Not only will your site’s traffic remain intact, but you will protect your SEO rankings from dropping due to broken links.
Along with the 301 technical nitty gritty, we will discuss real-world use cases and scenarios. Plus you’ll get some industry best practices on how to handle them.
What is a 301 redirect?
A 301 redirect permanently redirects a user’s request and the associated URL to a different URL. This communicates to web browsers and search engines that a page has been permanently moved.
The management of 301 redirects is an important aspect of technical SEO.
By redirecting visitors to the new location, 301 redirects help maintain an old URL’s SEO value, including traffic, rankings, and link equity.
They’re especially useful during site migrations or structural changes when the old URL is no longer needed. The new URL takes over the search engine rankings, and all new traffic is redirected to that page.
Another common use of 301 redirects is when you’re merging several pages into one. For example, consolidating various blog posts into a single page can reduce duplication issues and increase traffic to the new URL. By implementing 301 redirects, the new URL inherits the search engine rankings of the previous page and directs users to the updated content.
The 301 redirect helps to consolidate traffic to the new URL and reduces the duplication problem.
How does 301 redirect work
A 301 redirect transfers a vast amount of SEO value from the original page to the new URL. When a web browser requests the old URL, the server responds with the HTTP status code 301, directing the browser to the new location.
This process helps maintain search rankings, prevent 404 errors, and boost user experience. So it’s widely employed during website migrations, restructurings, or URL changes.
(It’s even used when someone types in an incorrect URL.)
The purpose is to make sure that, in the eyes of search engines such as Google, the site remains a credible, legitimate, and valuable entity. It should not lose traffic because of a restructure. It should become more authoritative as a result.
How does 301 redirect affect SEO?
If you use it wisely, a 301 redirect can spruce up your SEO and help you stay ahead of your competition.
It complements a lot of things and helps keep your site alive and in the rankings. Here are some effects it has on SEO:
Improves site performance and loading time
Properly executed 301 redirects can reduce HTTP requests, which results in faster load times. This is especially important for redirect chains, as lengthy processes like this can slow down sites.
Fewer redirects help improve your site’s performance and speed, retain visitors, and improve bounce rates. Google and all search engines prioritize user experience. So fast loading web pages can improve your rankings.
Preserving link equity
Link equity (also known as ‘link juice’) is the SEO value that a link from one page transfers to another.
In this case, we’re talking about link juice coming from backlinks. A 301 redirect will transfer almost all of that equity to the new URL, meaning that existing backlinks to your old URL will continue to link to your site, and your site will continue to benefit from the backlinks’ search engine rankings and positioning authority.
When you have valuable backlinks to your site, you certainly don’t want to lose them—you want to ensure you safely move them to your new site.
Without proper redirection, your site could lose all credibility and domain authority, forcing it to start from scratch. Credibility and domain authority are two of the most important factors in getting a good search engine ranking.
Preserving traffic
301 redirects are essential for maintaining traffic from high-authority sources like Wikipedia, major news outlets, social media, and other incoming links. These external links drive valuable traffic to your site, and losing it due to poor redirection can severely impact visibility.
Within your own domain, 301s are equally important for retaining internal link value and ensuring visitors can access updated pages.
Properly redirecting keeps traffic flowing from both external and internal sources. It also preserves SEO value and user engagement.
Preventing poor user experience
Encountering 404 errors from broken links frustrates users and can lead them to abandon your site. For search engines, frequent 404 errors signal poor site maintenance, negatively affecting rankings.
By implementing 301 redirects, you avoid broken links, guide users smoothly to relevant content, and maintain a positive user experience that supports SEO performance.
Preserving rankings
Google’s PageRank algorithm ranks pages based on relevance, and with recent updates, 301 redirects now retain nearly all of a page’s SEO value.
This means a 301 redirect effectively transfers PageRank from the original URL to the new one, helping to maintain competitive search rankings.
Properly managed, 301 redirects keep your site visible to users searching relevant keywords and reinforce your content’s authority across search engines. However, poorly executed redirects can slow page load times and impact rankings.
PageRank is an algorithm implemented by Google to rank web pages. Traditionally, upon receiving a 301 redirect, a web page would lose 15% of its PageRank; but thanks to Google’s recent tweaks, this loss is negligible now, so using 301 redirects helps you retain the PageRank of the original page and shifts its SEO value to the new one.
You can keep your new pages competitive in the search engine rankings, and your new website will remain visible to users searching for the relevant keywords simply because your original PageRank was high.
Being listed near the top of Google results gives you ‘Google juice’, a signal to other search engines that your content is trustworthy and authoritative. Google has updated its algorithms to reflect research showing that the PageRank loss in a 301 was essentially nil.
Conversely, poorly managed redirects can delay page loading, irritating users and leading to a loss in search rankings. According to Google, a one-second delay in page load can reduce conversions by 7%. This shows how the user experience directly influences business metrics.
When to use 301 redirect
When it comes to using 301 redirects, there are key situations where they’re essential for keeping your website running smoothly and ensuring a great user experience.
A simple rule to remember is that whenever you change an existing URL, setting up a 301 redirect is a good idea.
This helps prevent those frustrating 404 errors that can send users away from your site. Even if a page doesn’t get much traffic, redirecting it is still best practice.
Below, you’ll find some common scenarios where 301 redirects come in handy:
Migrating domains
When you migrate your site to a new domain, redirecting your URLs page-to-page with 301s helps preserve traffic and SEO equity so you won’t lose the site authority you worked hard to build up and the rank you fought to earn.
Domain migrations can be complicated, with lots of moving parts. With 301s, these redirects act as bridges to hold your SEO while you cross into the new site. If you don’t, you will likely lose traffic and your SEO footprint.
Changing website structure
Site reorganizations often require 301 redirects. Whether updating to SEO-friendly URLs, adjusting paths or slugs, or moving products and categories, a 301 redirect keeps traffic flowing. It lets search engines crawl new URLs without ‘404 Not Found’ errors.
URL changes may result from rebrands, restructures, or simple UI updates. 301 redirects are essential for a smooth transition, keeping both your audience and search engines informed.
Consolidating content
By redirecting overlapping or competing content to one single authoritative page, you’re simplifying the user experience and making it easier for search engines to understand the relevancy and structure of your content.
Take a bunch of pages that talk about the same or very similar topics but need to be ranked. You can take all that link equity and traffic and put it into one single page to improve your visibility and authority.
Phased website launches
If you’re launching a new site in stages, using 301s helps direct users from the old version of your site to the new pages of your new one.
This prevents users and search engines from getting lost during your transition and prevents a drop in traffic or your hard‑won SEO value.
A phased launch makes big projects manageable; you can make all your changes and then fine-tune them as needed with minimal disruption. Redirects are the hinges. Without them, both users and search engines would fall off the wheel.
301 best practices
Here are some tips on how to do 301 redirects that will really improve both the performance and rankings of your website:
Leave as few internal 301 redirects as possible
You want as many pages as possible to return a 200 (OK) status code, indicating that the page is live and functioning properly.
Minimizing internal 301 redirects reduces HTTP requests, leading to faster load times and an improved user experience.
Streamlining your site can also enhance the efficiency of search engine bots as they crawl and index your content. Think of it as shortening the paths through a maze to help users and bots navigate more easily.
Use 301 redirects for permanent changes
Any permanent changes to the URL must be accompanied by a 301 redirect, which says to the search engines that the move is permanent and that they should transfer the SEO value of the old URL to the new URL.
Without this, losses in search engine rankings and link equity are inevitable.
These permanent URL changes will also be helped by putting in place 301 redirects. As for temporary changes, you should avoid the use of 302 redirects where possible. They are not wholly passed on in PageRank and can also confuse the search engines over time.
Set your 301 ASAP to avoid losing traffic
If you delay your 301s, you’ll not only lose your SEO ranking but lose traffic. Set up 301s as soon as you permanently change your URLs to avoid repercussions.
If you act quickly to set up redirects, you can maintain your SEO value, ensure uninterrupted access to content, and minimize disruptions to user experience. Acting fast reduces the risk of losing valuable organic traffic and search engine trust.
Avoid redirect chains and loops
Redirect chains happen when a URL is redirected several times before reaching its final destination. At the same time, redirect loops send a URL back to itself or another URL in an endless cycle.
Both issues harm user experience and degrade SEO value. To avoid this, always redirect directly to the final destination URL.
Keeping your redirects clean and direct improves user experience and ensures faster page-loading times.
This will reduce your site’s bounce rate and positively impact rankings. Redirect chains can result in countless page-loading “hops” and, user experience aside, the longer the hops, the longer the loading times.
From a management perspective, minimizing your redirections and planning them smartly from the start is best.
Remove pages with 301 status codes from your sitemap
You will want to remove pages returning a 301 status code from your sitemap. This is because the page has already been redirected, and search engines don’t need to re-crawl the page, preserving your crawl budget for more critical areas of your site.
Make sure that you update your sitemap with the new URLs to facilitate indexing. Search engines are much better at indexing relevant parts of a site, the part that will most likely deliver a great user experience for the searcher.
From a technical point of view, a properly maintained sitemap sends the bots’ energy and computing power to where it is needed: to live content, not dead or duplicate pages.
Fix broken redirects
Broken redirects lead to 404 errors, which result in a poor user experience and negatively impact SEO. Use Similarweb’s SEO Audit tool to identify and address these issues promptly.
Regularly checking your site for broken redirects helps ensure proper functionality, benefiting both users and search engines. The absence of broken links signals to search engines that your site is well-maintained. Even a single broken link can disrupt user flow and indicate neglect to search engines.
Test your 301 redirects after creation
Every 301 redirect should be tested. After setting up a redirect, test it. The test itself takes less than a minute, and it will save you future headaches.
Tools that allow you to create a 301 redirect—like built-in options in all-in-one platforms or WordPress plugins—will include a feature to check the redirects you have created. You can also check manually by entering the old URL in the address bar to see if it redirects to the new URL. Using Incognito mode is a good idea, as it helps bypass caching issues.
Monitor your 301 links and web traffic
Given the importance of implementing 301 redirects, it’s equally essential to monitor them: ensure that all redirects function correctly, avoid 404 errors, and see which 301s can turn into 200 OKs.
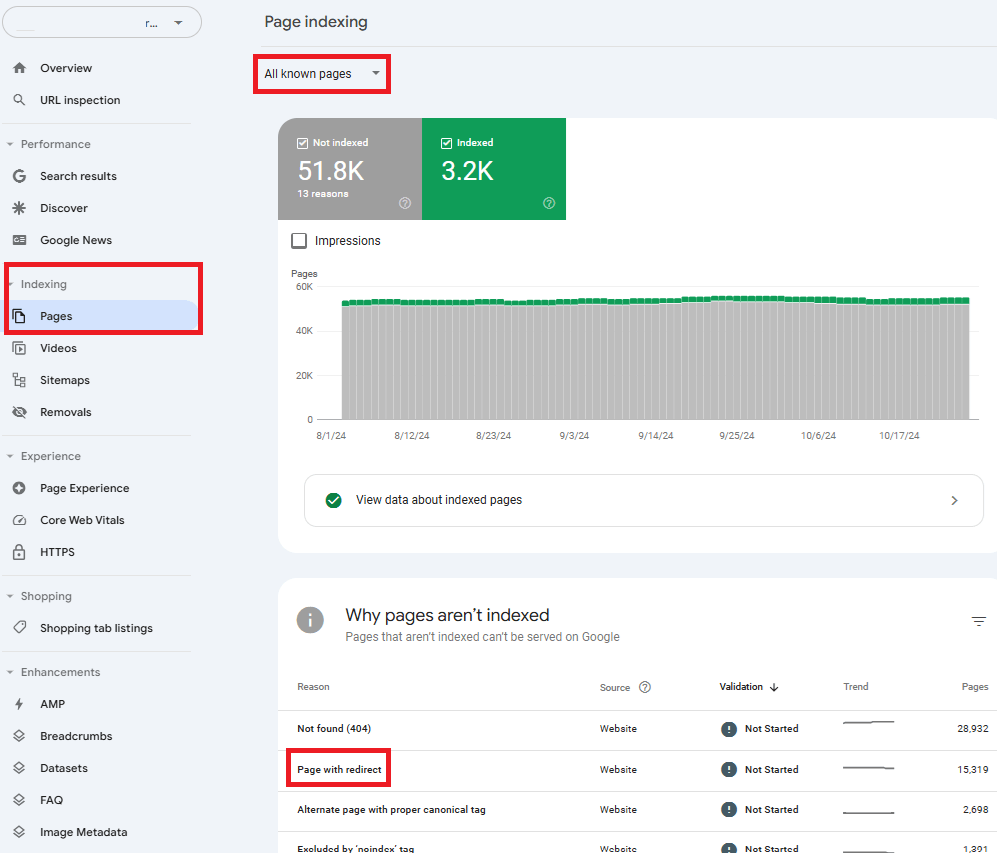
Google Search Console
You can find pages with redirects on Google Search Console under ‘indexing’>’pages’. GSC’s default is “all known pages”, and you can also filter by all submitted pages.
This check is helpful, but it has two main limitations:
- It only checks for the pages that Google detected, not all pages on your site. This means you’ll only be able to fix broken links, not prevent them in the first place.
- In the case of “all known pages,” the URLs will usually include a parameter (domain.com/slug/?parameter), and duplicate URLs will only differ by their parameter.
Similarweb Site Audit tool
Another way to find all the 301s on your site is by using Similarweb’s site audit tool. After updating your website, navigate to ‘SEO,’ then click on ‘Discoverability’ and ‘Redirections’ to view scores, issues, and trends related to redirection. This tool helps you ensure that your redirects align with your site’s SEO strategy at all times.
Pro tip: Don’t forget to check your website traffic to see how it correlates with your 301 redirects. A drop in traffic can indicate potential issues with your redirects, such as broken links or misconfigurations. Monitoring traffic trends helps you quickly identify and address any problems, ensuring your users remain engaged and your SEO performance stays strong.
How to redirect URLs
Whether your site’s URLs are changing or you’re fixing broken links and dead-end pages, here’s how to set up redirects on different platforms:
In WordPress
For WordPress users, you can follow a simple series of redirects by using the plugin redirection. Users don’t have to edit code themselves. Here’s how:
- Install and activate the “Redirection” plugin from the WordPress repository.
- Go to Tools > Redirection within your WordPress dashboard.
- Enter the source URL (old URL) and the target URL (new URL).
- Click “Add Redirect” to apply the changes.
- Check to make sure it worked.
When you follow these steps, visitors—real people or search engine robots—are promptly guided to the new URL. This maintains the integrity of your site and provides a smoother user experience.
HTAccess syntax
If your site is hosted on an Apache server, you can manage redirects via a .htaccess file. You can use this file to set server configurations to your requirements. Here are some examples:
Redirect a single page
Redirect 301 /old-page.html /new-page.html
Redirect an entire domain
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^oldsite.com [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://newsite.com/$1 [L,R=301,NC]
Use Regex for redirects
RewriteRule ^old-directory/(.*)$ /new-directory/$1 [R=301,L]
These commands provide a solid means of redirection by using the 301 status code (known as ‘permanent redirect’), so that all the SEO juice from the old URLs can be preserved.
IIS Redirection
For websites that are hosted on IIS (Internet Information Services), redirections are managed via the ‘web.config file’. This XML-based configuration file controls different settings of the web server. Below is a basic code sample for implementing a 301 redirect:
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<rewrite>
<rules>
<rule name=”Redirect to new URL” stopProcessing=”true”>
<match url=”^old-page.html$” />
<action type=”Redirect” url=”/new-page.html” redirectType=”Permanent” />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
This snippet will direct any requests for old-page.html to new-page.html, ensuring both users and search engines are appropriately redirected.
How to redirect an entire domain
In the case of site migration or rebranding, a domain-wide redirection is significant to pass on the traffic your website already receives and the SEO value it already possesses.
Not doing so would lead to a drastic drop in your search rankings, an enormous loss of users who are not aware of your newly launched site, and so on.
There are a few available techniques to achieve a domain-wide redirection, which can be applied in different circumstances and under different hosting environments:
Web server (Apache/NGINX) rewrites
For Apache servers, you can redirect an entire domain by configuring the .htaccess file:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^olddomain.com [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://newdomain.com/$1 [L,R=301,NC]
This configuration makes sure that any traffic to olddomain.com is permanently redirected to newdomain.com while preserving query strings and URL paths.
For NGINX, domain-wide redirections are managed by editing the server block configuration file:
server {
listen 80;
server_name olddomain.com www.olddomain.com;
return 301 $scheme://newdomain.com$request_uri;
}
This example snippet does a permanent (301) redirect from an old domain to a new domain, while retaining the resource path and allowing the user’s continued access to the resource.
Hosting control panel
Most hosting providers (cPanel, Plesk, etc) come with default functionality for domain redirects that don’t require any manual configuration of the server. Each hosting provider has its own how-to guide, but here are the general steps:
- Log in to your hosting control panel.
- Go to the redirect section, which is often found under domains or URL settings.
- Specify the old domain and the new domain in the form fields.
- Save the changes to implement the redirect.
This straightforward method is user-friendly and guarantees efficient redirection, which helps maintain the migrated site’s accessibility and SEO value.
Server-side app redirect
In the example provided below, the server-side app redirect is implemented with PHP, instructing the server to forward users to a new URL.
<?php
header(“Location: http://newdomain.com”);
exit();
?>
This works well because it is handled on the server level before the page has been rendered. It also maintains user experience and search engine indexing continuity.
WordPress-based redirects
Thanks to plugins, WordPress implementations can be made using redirects that apply to the entire domain. For instance, the ‘Redirection’ plugin can be used to achieve this:
- Install and activate “Redirection” from the WordPress repository.
- Access Tools > Redirection in your WordPress dashboard.
- Set the source field to “/“, indicating the whole domain, and specify the new domain URL as the target.
- Click “Add Redirect” to apply.
This way, all the traffic to the old domain is redirected to the new domain, preserving the user experience and the ranking with search engines.
How to fix 301 redirect issues
Although implementing 301 redirects is fundamental to good SEO practices, problems can still crop up. Here are the most effective ways to get them back on track:
Turn your old 301s into new 200s
It’s best to replace old URLs with new ones across your website to avoid unnecessary redirects. In more technical terms, wherever you can replace a redirected link (301) with a directed link (200) – do it.
Direct links reduce load times and improve SEO effectiveness. Regularly auditing your content helps keep all links current and functional.
Resolve redirect chains
Make A → B → C chains simpler by converting them to A→ C. If you have a page that is linked to more than one page, try to get rid of the extra links to reduce lag time and maintain SEO efficiency.
Align redirect loops
Make sure there is no URL pointing to itself, creating a loop that can confuse search engines and users alike. Look in server logs for clues about any loops.
Correct broken redirects
Regularly audit your site to look for useless or broken redirects that chain up to 404 pages. Fix them by updating the target URLs or, if they were added in error, removing them completely. Keep your redirects clean and usable for both users and algorithms.
Use an SEO audit tool
To detect and fix these issues run regular SEO site audits. Similarweb audit tools can help you detect issues with your 301 redirects. Often it pays off to regularly monitor and optimize the website through such means.
Don’t let poor redirections affect your site’s performance
Knowing what a 301 redirect is and how it can work for your site is an important SEO and user-experience tool to master. Learn how to manage your redirects so that you can hold on to your search engine rankings and keep the experience of navigating your site as smooth as possible.
So, are you ready to boost your site’s performance? Try Similarweb’s SEO tools to get a comprehensive view of your performance and how your redirects impact it. Then optimize for better results.
FAQs
Is 301 an error?
No, it’s not an error. But if you see a 301 on your site and the page is now live permanently, you want to update that URL to a 200 status so that the page can be accessed directly with no redirects. This improves user experience as well as SEO performance.
Why are 301 redirects important for SEO?
A 301 redirect passes on the link equity (the ranking power) and authority of the old URL to the new URL, allowing it to maintain its ranking in the search results. It also avoids 404 errors, which improves user experience and signals to search engines where the content can be found.
What is the difference between a 301 and a 302 redirect?
A 301 redirect signifies a permanent move—bringing all the link equity with it to the new URL. A 302 redirect indicates a temporary move, with the expectation that you’ll return to the original URL in the future. So, a 301 redirect should only be used for a one-time, permanent move.
Can a 301 redirect affect site performance?
When properly executed, 301 redirects will also limit the number of HTTP requests and improve site performance and loading times because they don’t create redirect chains.
How do I know if my 301 redirect is working?
You can check that your 301 redirects are functioning properly, and sending traffic to the correct websites, using tools such as Google Search Console and Similarweb’s SEO audit tool.
The #1 keyword research tool
Give it a try or talk to our marketing team — don’t worry, it’s free!