Keyword Mapping in 4 Easy Steps: Guide + Free Template

“It’s easy to forget that a site doesn’t just ‘rank’ on its own, it ranks for what it’s relevant for.” – John Mueller
How do you signal to search engines that your content is relevant to user queries? One effective method is through strategic keyword placement. But how do you establish that your entire site holds relevant answers to various user queries?
The answer: Keyword mapping.
In this post, I’ll explore keyword mapping and how you can use it to establish your content as relevant to user searches, ultimately improving your search engine rankings.
What is keyword mapping?
Keyword mapping is the process of pairing target keywords with specific pages on your website. By pairing keywords to pages, you signal to search engines that these pages contain relevant information that answers the search intent behind the target query. Typically documented in spreadsheets like Google Sheets or Excel, this process applies to almost all site content, including landing pages, product pages, and blog posts.
Why is keyword mapping important?
By mapping all pages and the keywords they target, you can:
- Establish keyword relevance across your site
- Group your keywords based on topic and search intent
- Map out your internal linking strategy
- Record your metadata and on-page elements per page
- Avoid keyword cannibalization
How to do SEO keyword mapping in 4 easy steps
You must assign a primary keyword or keyword cluster to every page on your site. Here, a keyword cluster consists of up to five closely related keywords with similar search intent.
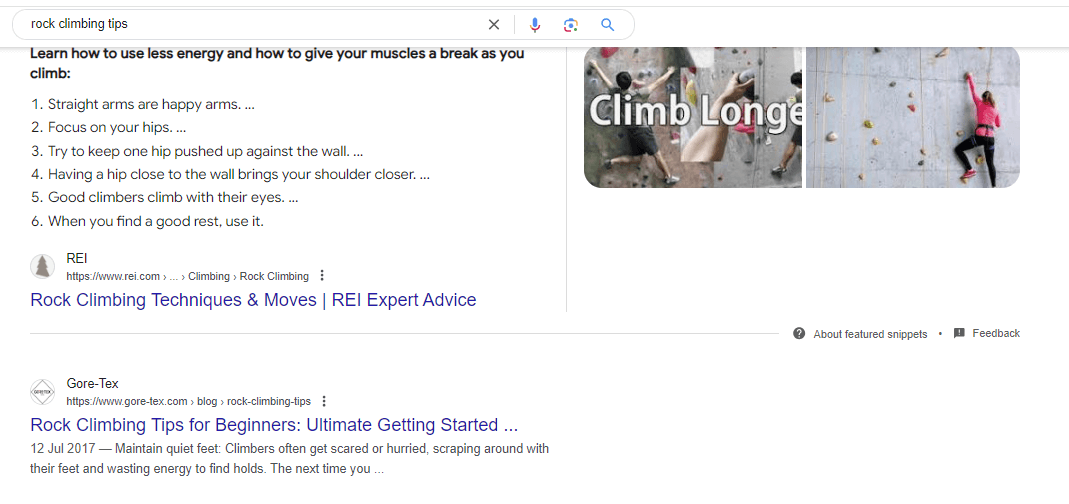
Search intent refers to the user’s purpose behind a search query—what question they want answered or what information they’re seeking. The easiest way to understand search intent is to Google your target keyword and analyze the SERP. This will show you:
- What answers Google considers relevant to the query
- What format the answer should be in
- What media users are interested in
For instance, below, the Featured Snippet shows us that users are looking for blog content that includes a number of tips formatted as a list.
To create a long-term SEO plan designed to generate significant traffic, your keyword mapping process should extend beyond simply matching keywords to existing pages. Here are the steps you should follow:
1. Find keywords (and related keywords) you want to rank for
Begin by conducting thorough keyword research on your entire niche to gather a comprehensive list of user queries related to your topic. This is a crucial process that requires time and attention to detail.
There are two primary ways to find all of the keywords in your niche:
A. Use a keyword generator
Start by finding a seed keyword. This is a broad phrase that represents the core concept or topic relevant to your site.
Finding the right seed keyword takes a little brainstorming and experimentation. The main challenge is finding a keyword broad enough to bring you a large number of keywords related to your niche. But, if you go too broad, you risk finding thousands of irrelevant keywords. If you go too narrow, you might not find enough keywords.
For instance, if I was creating a site for a site dedicated to organic gardening basics, the keyword:
- Outdoor sports is too broad and covers an enormous range of subtopics, making it difficult to focus on a specific niche or target audience
- Rock climbing is perfect because it’s specific enough to generate relevant keywords but not so narrow that it limits the potential for expansion
- Rock climbing safety gear is too specific to generate related keywords.
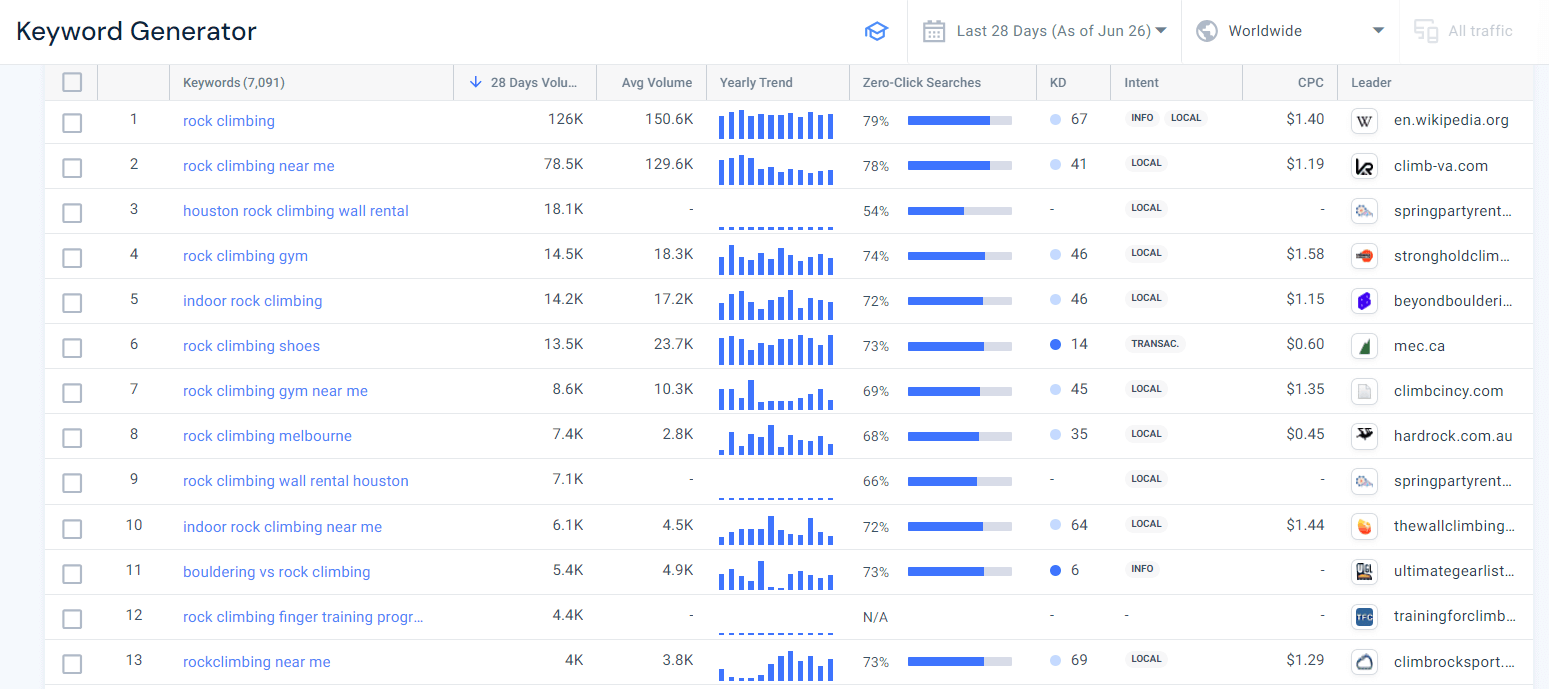
Once you’ve found a good seed keyword, use it as a starting point to generate more specific, related keywords. Drop your seed keyword into your keyword generator to uncover a large volume of niche-related keywords. Then, filter these results to find the most relevant keyword ideas for your content.
Below, I entered the seed keyword ‘rock climbing’ into the Similarweb Keyword Generator, and the tool returned thousands of results.
The next step is to find relevant keywords for my pages by using filters to help you find:
- Head terms, which are high-volume keywords that represent a topic as a whole
- Long-tail keywords
- High competition keywords
- Low competition keywords
B. Use a competitive research platform
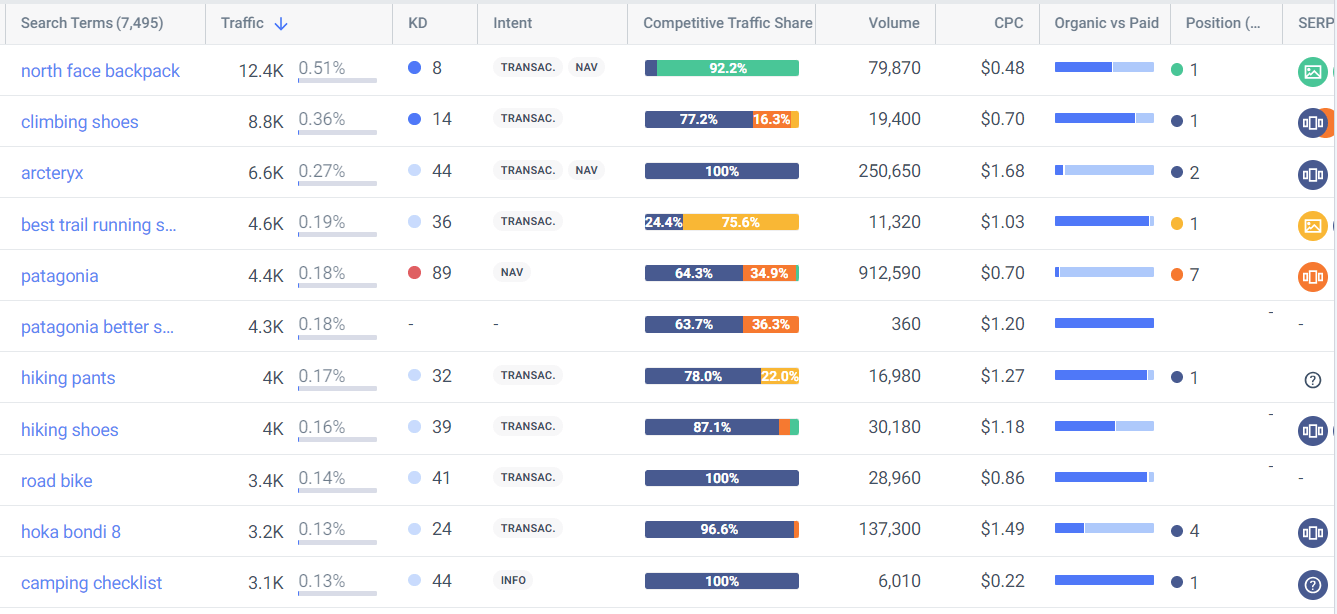
Researching your direct competitors is one of the most effective ways to identify target keywords. These competitors are already ranking for content in your niche, and you may discover they’re targeting keywords you haven’t considered.
Using the Keyword Gap tool, I analyzed outdoor sports brand rei.com and three of its competitors. The image below shows a visual representation of each site’s keyword market share and their overlaps.
This tool provides value beyond showing keyword overlaps. It allows you to:
- Prioritize keywords targeted by all sites
- Expand your search market share by targeting your smallest competitors’ keywords
If your site lacks substantial organic traffic, start by targeting keywords that all competitor sites are ranking for. Once you’ve covered those keywords, you can expand your keyword coverage based on what makes sense for your business.
2. Structure your keywords
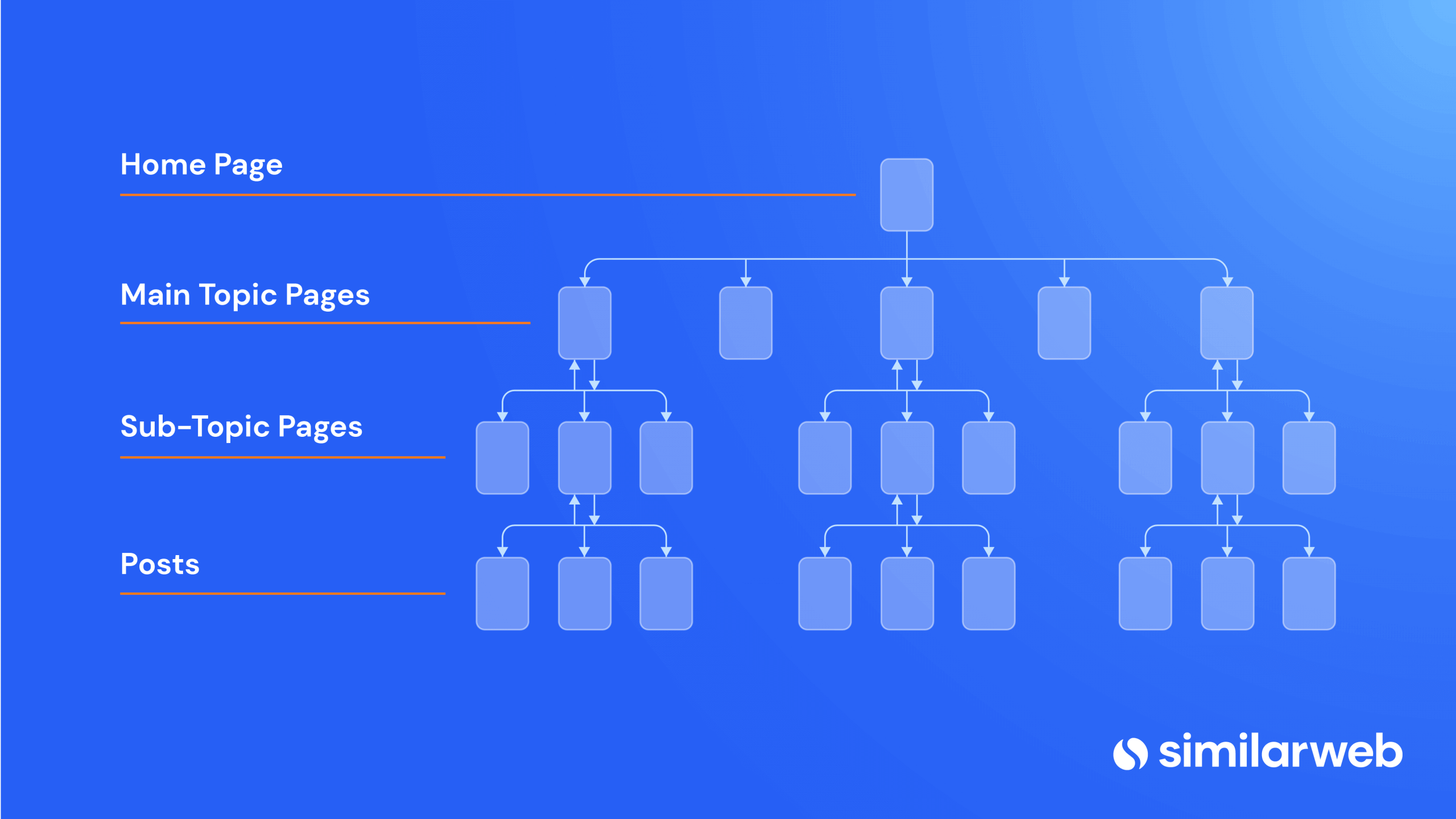
Gathering a large volume of niche-related keywords is just the beginning. The next crucial step is organizing these keywords into topics and subtopics. This structure will help users to find content on your site. Also, search engines use your site structure to understand what your content is about.
Your structure should inform how you set up your:
- URL folder structure
- Menus
- Breadcrumbs
There are three steps to create order out of your keywords:
Divide your keywords into broad categories
Sort your keywords into broad categories. If you get too specific at this stage, you’ll end up with too many categories, which will make navigating your content difficult.
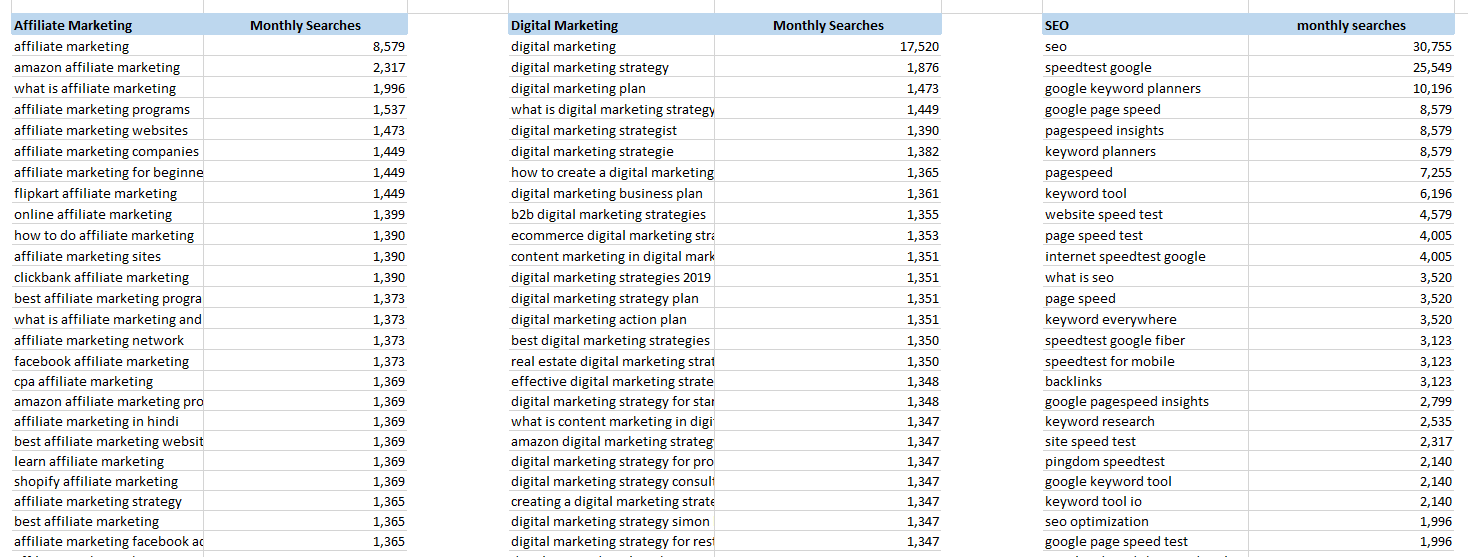
For example, if I was researching online marketing, my categories might include:
- Affiliate marketing
- Digital marketing
- SEO
- Content marketing
- Social media marketing
- PPC
Group keywords under each category, removing duplicates. These categories can also be the top-level site folders and menu links if relevant.
Divide each category into clusters
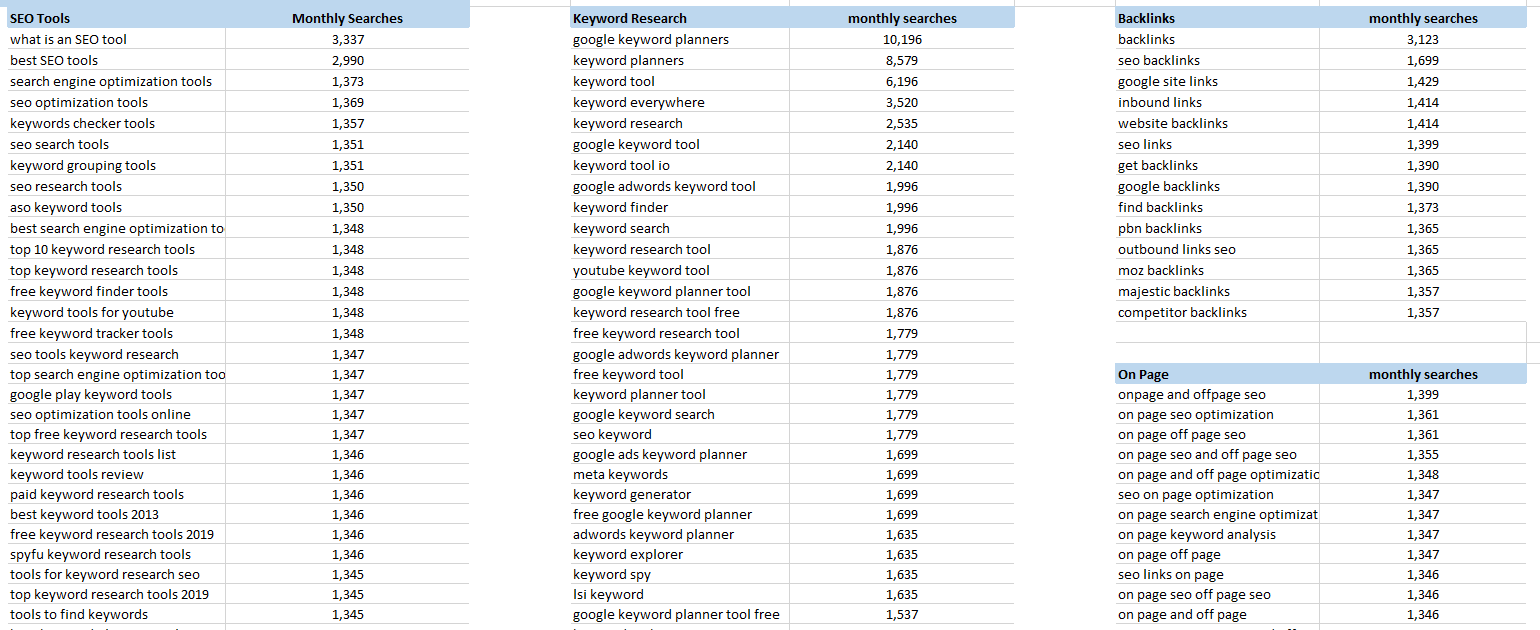
Now that I have broad categories with comprehensive keyword lists, I can divide each broad category into topical clusters.
Using the online marketing niche mentioned above, let’s break down the SEO category further based on SEO keywords:
- SEO tools
- Keyword research
- Backlinks
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
Each of these clusters represents a subtopic and should be targeted separately.
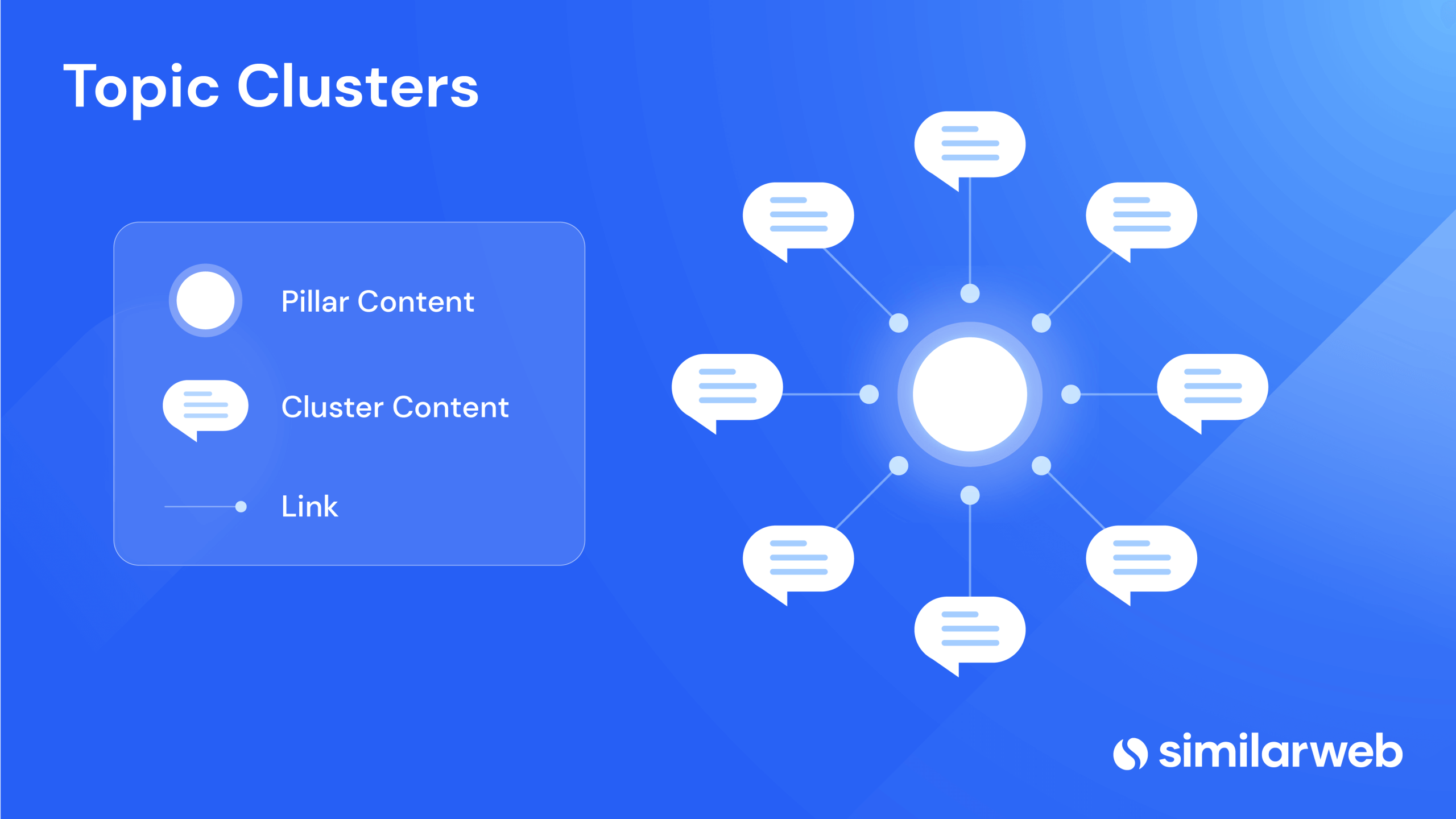
As a best practice, I usually sort my subtopic keywords into head terms and long-tail keywords. Content targeting these terms is called pillar content.
However, head terms are highly competitive, making it difficult to rank for them without supporting long-tail content. To maximize the effectiveness of my topical clusters, I link between head-term content and long-tail content.
For example, if I was creating an on-page SEO cluster, the pillar could be called ‘Comprehensive Guide to On-Page SEO.’ Supporting long-tail content might include:
- Optimizing Titles and Meta Descriptions
- How to Write SEO-Friendly Content
- Image Optimization for SEO
- Internal Linking Best Practices
Divide your keywords by search intent
Once you’ve divided your categories into topics, break your topics down into search intents. Each search intent represents a question that users type into the search bar.
Since people are unique, they tend to find different ways to search for the same thing, resulting in many keywords with the same intent. Grouping your keywords by search intent will ensure that you don’t create more than one piece of content that answers the same user query.
Here is an example of keywords with the same intent:
- Things to do in Paris
- Top Paris activities
- Best things to do in Paris
3. Create a keyword content plan
It’s time to map out the keywords you want to target. You can use our keyword map template or create your own.
In general, your keyword maps should include:
| URL | Page | Intent | Keyword 1 | Search volume | Keyword 2 | Search volume | Keyword 3 | Search volume |
- URL: Includes all the URLs on your site
- Page: Includes the name of the page
- Keyword: Includes the target keyword of the page
- Search volume: Includes the average search volume of the target keyword
- Search intent: Not a must, but I like adding it for better keyword alignment
Your goal is to develop a content plan based on the research from the previous steps, including keyword clusters and content structure. Begin by adding all the keywords you aim to target to your document. If you have keywords with the same intent, cluster them together for a single piece of content.
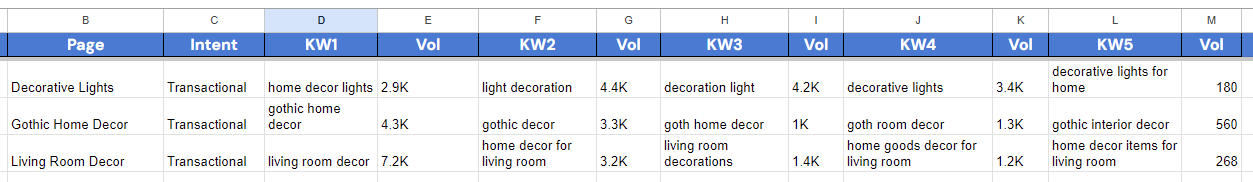
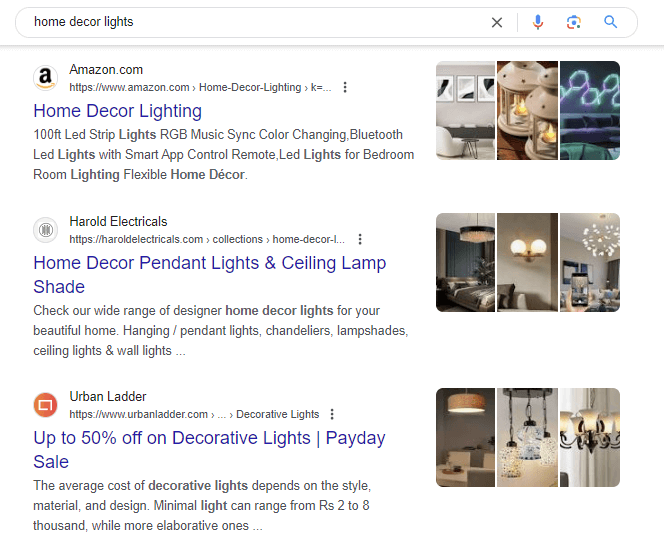
For example, here’s how I might start mapping out keywords for a home decor site:
Notice that I’ve omitted the URL column, as these are keywords for future content. Also, notice that I included five keywords per row, each sharing the same search intent. For a decorative lights page, I’ve included:
- home decor lights
- light decoration
- decoration light
- decorative lights
- decorative lights for home
This indicates that the plan includes creating a page titled “Decorative Lights” to target these keywords. Repeat this process for all the keywords you identified in the previous steps. Make sure you segment your keywords into appropriate categories and clusters.
This approach helps you organize your content strategy and guarantees each piece of content targets a group of closely related keywords with the same intent.
4. Map out your current site
With your content keyword map complete, the next step is to create a new keyword map to record your site’s live URLs.
- Add current URLs to the URL column
- Add target keywords for each page
- Update all pages to include your target keywords
As a side note, if you are changing your site structure based on your new keyword hierarchy, make sure to first redirect your pages to fit your new site structure.
Whenever you add a new page to your site, make sure to add the additional page to your keyword map. Mapping your pages this way will save you hours of work and help prevent cannibalization. With all of your keywords mapped out, you can easily make sure that any internal links that point to these pages have anchor text that includes one of your target keywords.
Keyword mapping: From chaos to content clarity
Keyword mapping is a vital part of any SEO strategy. Researching the keywords in your niche and breaking them down into a logical structure allows you to build out content structured in a way that users and search engines love.
In order to get started, you must have the right tools:
- A keyword research tool that gives you granular data
- A competitor research tool that uncovers your competitors’ keyword targeting strategy
FAQs
What is keyword mapping?
Keyword mapping is the process of matching target keywords with specific website pages.
What is the benefit of keyword mapping?
Keyword mapping is beneficial as you can track the efforts of your SEO activities, ensuring that you drive traffic to your website.
How does Similarweb help you with keyword mapping?
Similarweb will help you research keywords in your niche with its:
- Granular keyword data
- Powerful competitive analysis tools
How do I create a map for keywords?
You can create a keyword map in a few steps:
- Find the right keywords and related terms
- Select keywords that have the right search intent
- Group related keywords and use them based on search intent
- Structure your content to include keywords throughout the website hierarchy
The #1 keyword research tool
Give it a try or talk to our marketing team — don’t worry, it’s free!