HTTP vs. HTTPS: Why Securing Your Website Matters More Than Ever

The battle between HTTP and HTTPS is more than just a technical choice—it’s about safeguarding your website, boosting SEO rankings, and building trust with your users. While HTTP was once the standard, HTTPS is now the secure and preferred protocol.
In this blog, we’ll break down the key differences between HTTP and HTTPS, why HTTPS is the better choice for modern websites, and how it can positively impact your site’s security, performance, and search engine visibility.
Let’s get started.
What is HTTP?
HTTP is an application-layer protocol for distributing data via the Internet. It specifies how information related to the web (web pages, images, style sheets, scripts, etc.) should be transmitted. HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It is a request/response protocol that operates on web clients and servers.
How does HTTP work?
HTTP is a request/response protocol that operates by the client (in the case of a website that’s a browser) sending messages to a server. For example, let’s say you type a URL into your browser. The browser then sends an HTTP request to the server. The server processes the request and sends back an HTTP response with the content you requested (a web page, an image, or a document to download, etc).
The most common HTTP responses include 200 (OK), 301 (Moved Permanently), 404 (Not Found), and 502 (Bad Gateway) to notify users and developers of the status of their requests.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is a protocol built on top of HTTP, adding SSL/TLS security encryption to ensure that whatever is being transferred via HTTP remains private and secure.
HTTPS is the mechanism that needs to be added to ensure that sensitive information such as login credentials and payment details, among others, are secured on web pages and apps.
How does HTTPS work?
HTTPS works in pretty much the same way as HTTP, but it’s wrapped in a cloak of secrecy, courtesy of SSL/TLS. If a website wants to run HTTPS at all, it needs to get an SSL/TLS certificate from a Certificate Authority (CA), so that it can set up an encrypted channel directly with your web browser. This allows the site to know for certain that the data you send it is confidential and unaltered.
Some of these steps involve checking that certificates are genuine and agreeing on keys so that an encrypted channel can be set up, which then wraps all your data in a secure layer that guards it against eavesdroppers and meddlers.
HTTPS vs. HTTP: What’s the difference?
This is a common question online, and the answer is crucial for anyone with a website—whether it’s for business or personal use. Understanding the key distinctions between these two protocols is essential for protecting your site and improving its performance.
Let’s begin by exploring the technical differences between them:
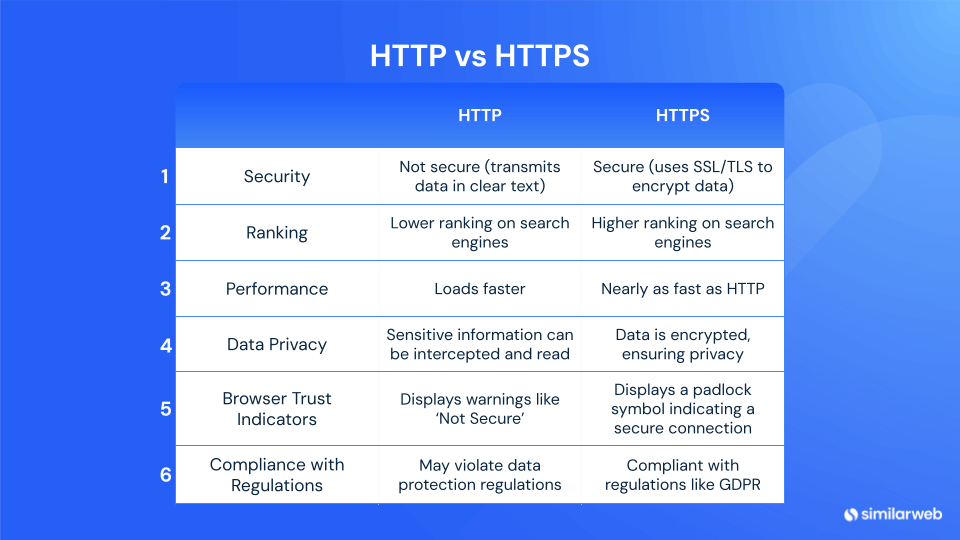
Security
HTTP websites transmit data in the clear, which means that an adversary could wiretap the connection and eavesdrop on the data.
An HTTPS website uses SSL/TLS to encrypt the data, meaning that it is private and cannot be eavesdropped on. It is also authenticated (i.e., the other end of the connection is verified as who it claims to be), and data is protected against tampering (if an attacker were to try and insert or alter data in the stream, they would get caught – and would probably be stopped). This, in part, helps to prevent attacks such as the man-in-the-middle.
Increased organic reach
Using HTTPS can significantly boost your website’s visibility in search engines. Search engines like Google prioritize secure sites (those using HTTPS) over non-secure ones (HTTP), meaning HTTPS sites are more likely to rank higher in search results. This improved ranking can lead to more organic traffic, as users tend to trust and click on secure sites.
Additionally, implementing HTTPS is considered a best practice for on-page SEO and contributes to the overall technical SEO health of your site. The secure connection it provides sends a positive signal to search engines, enhancing your site’s credibility and helping to maintain or improve your rankings.
Performance
HTTPS was slower initially (because there were more overheads involved in the encryption and decryption), but this has been mitigated by better internet protocols such as HTTP/2, which have features like multiplexing (that is, everything is done at the same time), header compression, and better use of TCP connections. Web traffic is now almost as fast over HTTPS as it is over plain HTTP.
Data privacy
Another major difference between HTTP and HTTPS is encryption. Information transferred via HTTP is in plain text, which means that all your sensitive information – for example, a username and password you used to log in to a website – can be monitored, intercepted, and read by a third party along the way. With HTTPS, this data is encrypted and remains private.
If you’re posting user data or taking payments from your users, HTTPS lets sensitive data flow through without anyone snooping on it. Even if it is, they can’t understand it. This extra privacy helps to build trust.
Browser trust indicators
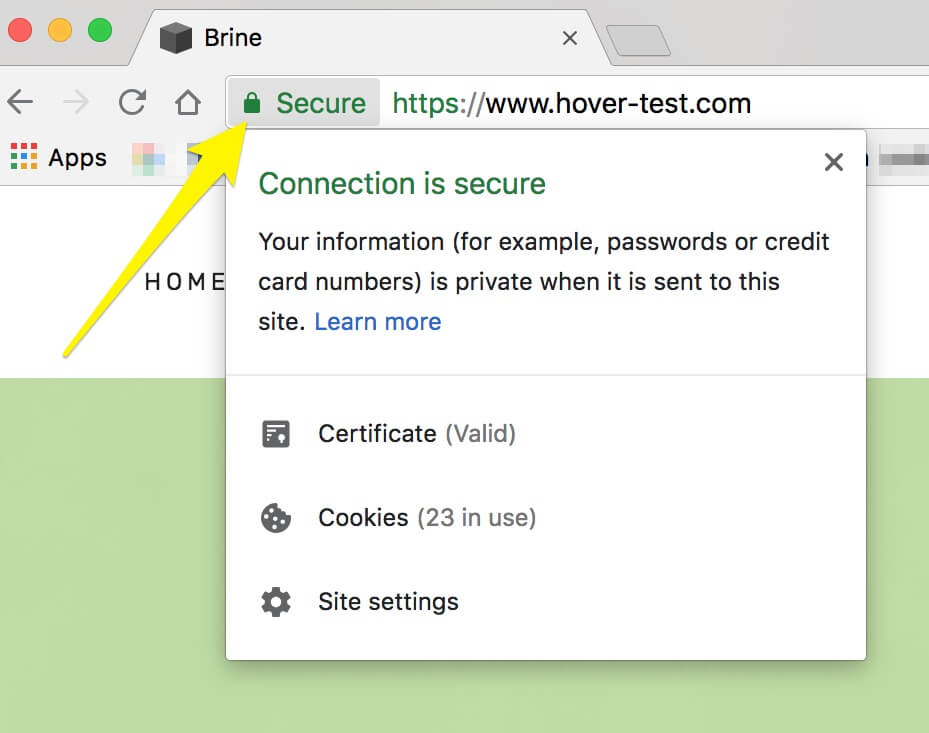
The historical development of browsers has enlisted a whole host of visual indicators to build trust in the visitor’s eyes. Sites using HTTPS will display a padlock symbol in the address bar with the word ‘Secure’ or the name of the business, depending on the type of SSL certificate installed.
Sites that are simply HTTP will show a warning like ‘Not Secure,’ which, depending on the type of website, can either stop a visitor in their tracks or give them pause before submitting any personal information. Trust indicators embedded in the HTTPS protocol help guarantee that sites operating under this banner are, in fact, secure.
Compliance with regulations
In addition, increasing data protection regulation, such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), makes HTTPS no longer a luxury. Websites are legally required to transmit sensitive user data in an encrypted manner, and due to these legislative measures, HTTPS – despite not being perfect – is the easiest, most compliant way to do so.
Considering the potential legal consequences due to data breaches, failure to migrate to HTTPS could result in hefty fines and the risk of losing customers’ trust. As a result, for enterprises that rely on doing business online, it has become a technical necessity to switch to HTTPS, as well as a legal one.
HTTPS benefits for your website
Using HTTPS on your web server offers a host of advantages that are essential for web security and user trust, backed by decades of studies and best practices that have made HTTPS the default for most sites.
Data security
A key benefit of HTTPS is data security. The data flowing between the browser and the server isn’t in plaintext as it is in HTTP. It’s encrypted using SSL/TLS (secure sockets layer/transport layer security) protocols. This encryption makes it much harder for malicious actors to steal sensitive data, like a user’s password or credit card number.
HTTPS is quite important for ecommerce sites and all sites that handle any form of personal user information. It’s a signal to your users that their data is safe. Proper encryption means that even if data is intercepted, it can’t be read or used for malicious purposes – it fundamentally keeps data confidential and protects its integrity.
Protection against cyber threats
HTTPS protects against man-in-the-middle attacks, and data breaches – really, who knows what else. With HTTPS, all data transmitted between the user and the server is successfully encrypted. This makes HTTPS one of the greatest tools against the serious assault on user information. With HTTPS, user data is protected against any kind of hijacking or tampering while it’s in transit, be it a user’s password, social security number, or other confidential information. The data exchanged between client and server is also kept secure from unauthorized third-party access, and its integrity remains intact.
Since attacks on the internet are becoming more sophisticated, now is a good time to start implementing HTTPS if you want to continue to offer a safe service to your users – those extra lines of encryption help keep your users’ data safe from prying eyes and attacks. Adding that extra layer of security against data interception and alteration is a real, actionable step you can take today.
Builds user trust
HTTPS builds trust by displaying a padlock, signaling a secure connection, which encourages users to share personal information or complete transactions. It also enhances SEO by sending positive ranking signals to search engines and building a strong online reputation.
Beyond trust, browsers now warn users before accessing non-HTTPS sites, making it harder to proceed. Since July 2018, Chrome flags all HTTP sites as “not secure”, meaning sites without HTTPS risk losing visitors, traffic, and engagement before they even arrive. HTTPS ensures both credibility and access.
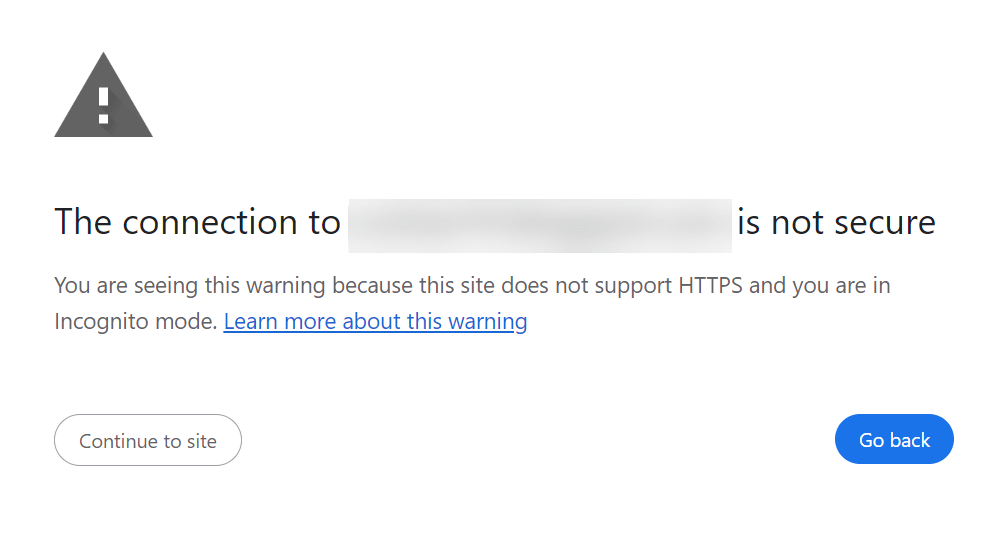
This site doesn’t have HTTPS, so this is the message you get when you try to access it. Be smart, support HTTPS.
Improves SEO rankings
HTTPS improves SEO by boosting your site’s search rankings. Google favors HTTPS, giving secure sites higher visibility in search results. This means more organic traffic and better engagement, as users trust secure sites. Moving to HTTPS can increase traffic, improve user trust, enhance security, and boost conversions—all key factors that improve your overall SEO.
How to migrate to HTTPS
When transitioning from HTTP to HTTPS, there are several important steps you must take to ensure a smooth migration that won’t compromise your data and will also make your site more secure and faster. Each one of these steps is important for a fully secure and SEO-friendly site.
Get SSL certificate
Start by acquiring an SSL certificate from your server provider, as it enables HTTPS. For WordPress users, getting an SSL certificate from the hosting provider is ideal, but you can also use plugins like Really Simple SSL for a quick setup. The SSL certificate encrypts all data, ensuring security during transmission. There are different types of SSL certificates – Single, Wildcard, and Multi-Domain. Most hosts recommend one type, which is sufficient for SEO purposes.
Install the SSL certificate
After obtaining the SSL certificate, install it using your hosting provider’s control panel (e.g., cPanel or Plesk), where the process is usually straightforward. Make sure to cover all subdomains and primary domains. After installation, configure your HTTP headers to prompt browsers to switch from HTTP to HTTPS. Proper configuration is crucial to ensuring your SSL certificate works correctly.
Create a 301 redirect
Implement a 301 redirect from HTTP to HTTPS to ensure all links are directed to the secure version of your site. This maintains SEO value, avoids broken links (404 errors), and guarantees users are redirected automatically. Configure the redirect in your server configuration files (e.g., .htaccess for Apache servers or web.config for IIS servers).
Update sitemap
Once HTTPS is in place, update your sitemap to reflect the new URLs. Use Google Search Console to resubmit your updated sitemap.xml, ensuring that search engines crawl and index your site’s correct URLs. This prevents issues like missing or improperly indexed pages and helps maintain a healthy domain profile.
Pro tip: Add a Google Search Console property
If you use only a domain property – this stage is not for you. But if you use URL Prefix properties, it’s wise to also add your domain in Google Search Console. This will allow your traffic for HTTP and HTTPS to be tracked separately, rather than being aggregated into the single domain property.
It’s also easier to track each of these versions separately if both HTTP and HTTPS traffic are monitored concurrently. Slicing and dicing data this way helps to maintain a clear perspective of how each works and what to do next.
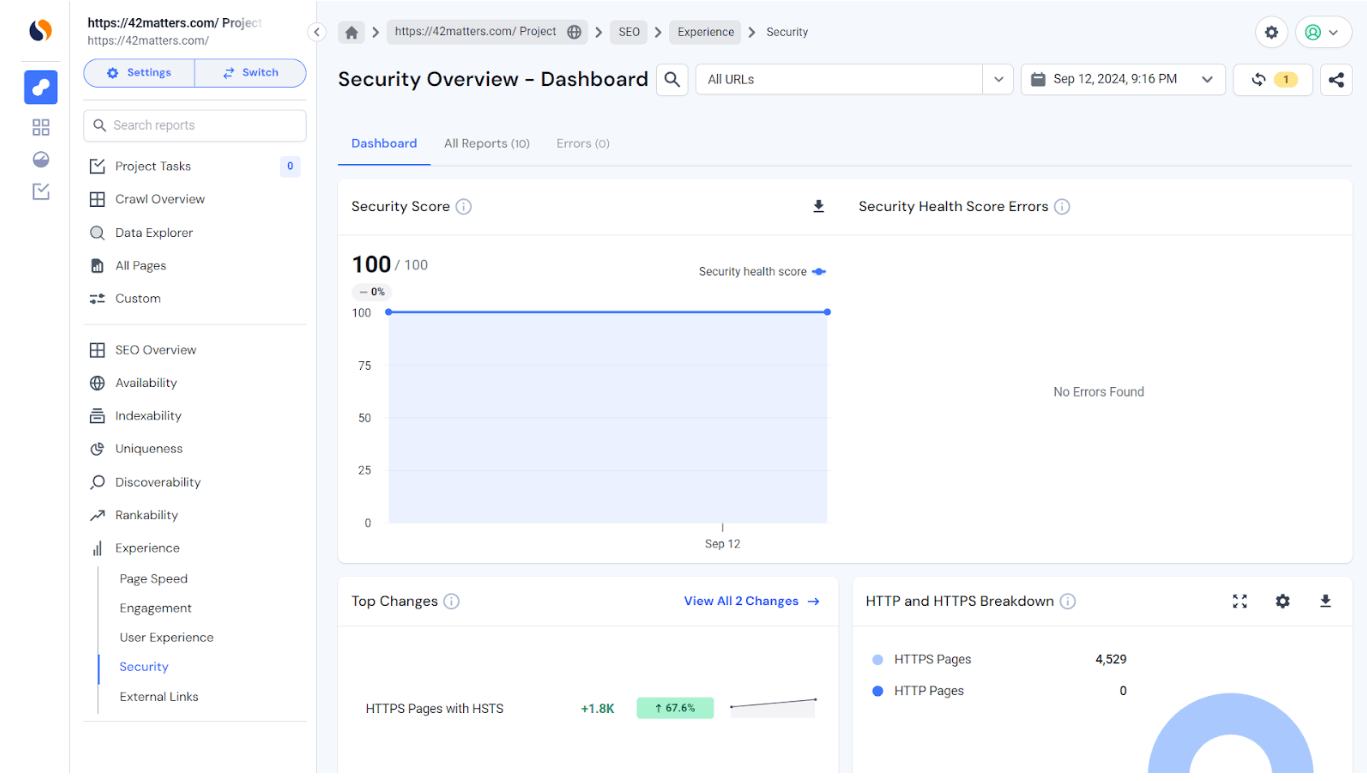
Monitor issues
Once you migrate to HTTPS, it’s important to check periodically for errors. Similarweb’s Site Audit tool can be used to assess your site. If you are logged in to this platform and on your crawled project, go to SEO > Experience > Security where you’ll discover information on HTTP/HTTP breakdown, HTTPS issue trends, and more.
This is just one example of how continuous monitoring and regular SEO audits can help keep your HTTPS site secure and at a high level of performance. It allows you to catch any problems before they derail your user experience or negatively affect your SEO performance.
Similarweb Site Audit tool to help you maintain the integrity of your site is an added bonus. Knowing that your site is always in great shape will only strengthen your site’s integrity in the long run.
Transition to HTTPS easily with Similarweb
Switching to HTTPS brings essential benefits like enhanced security, increased user trust, and better SEO rankings. Similarweb’s powerful SEO tools and insights make the process effortless.
Get a detailed report on your internal links, identify issues, and find clear solutions to fix them. Secure your website and optimize it for organic search today.
With Similarweb’s reliable SEO tools at your side, your next big digital growth opportunity is just a step away.
FAQs
Is HTTPS secure?
Yes, HTTPS is secure. It uses SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt data traffic between a browser and a server. Since only the intended parties on either end possess the key to decrypt the data, it’s very difficult for anyone in between to intercept it (as they could with HTTP) or alter what’s being transmitted (commonly known as a “man-in-the-middle” attack).
What is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS?
HTTP sends data as plaintext and is much less secure. HTTPS, on the other hand, encrypts data with SSL/TLS, protecting it from potential eavesdroppers or intruders.
Does HTTPS affect SEO rankings?
Yes, HTTPS does impact SEO performance. Having an SSL certificate is a ranking factor, and Google Chrome marks HTTP sites as “not secure,” which can deter users from accessing them.
Can I use HTTPS for all types of websites?
Yes, HTTPS should be implemented on all websites, regardless of whether they handle private information. It improves security, trust, and SEO rankings.
What are common HTTPS issues to watch out for?
Common HTTPS issues include mixed content warnings, untrusted certificates, and expired certificates. Most of these can be detected through regular monitoring.
Track Gen-AI And Organic KPI's On The #1 SEO Platform
Give it a try or talk to our marketing team - it’s free!